The Loom is Spinning: Enter the Norse Saga Engine

The sagas of old were carved in bone and stained in red—now, they are forged in code.
The Norse Saga Engine is a groundbreaking RPG experience that uses real-time AI to weave a living, breathing Viking world around your every choice. This isn’t a sanitized fantasy; it is a hyper-realistic dive into the grit of the Viking Age, where history, folklore, and the whispered secrets of the runes collide.
What Awaits You:
- True Authenticity: Built on a foundation of genuine Norse lore, religious practices, and the complex social structures of the era.
- Visceral Interaction: Advanced, adult-oriented AI characters that respond with human-like nuance, memory, and depth.
- The Power of Seiðr: A low-fantasy world where magickal practices and Norse spirituality aren’t just mechanics—they are the atmosphere.
- Novel-Quality Narrative: Every session generates an interactive historical fiction masterpiece, tailored to your path.
The Norns are weaving a new thread, and the architecture of the soul is being mapped. This project is developing rapidly—prepare to claim your place in the saga.
Stay tuned. The high tide is coming.
Vikings and AI Working Together to Stop Trump

“Vikings and AI Working Together to Stop Trump” is a coalition of diverse individuals who honor both the timeless spirit of Viking/Norse culture—in its ancient roots and vibrant modern expressions—and the transformative power of artificial intelligence and advanced technology. We stand united against authoritarianism, particularly the Trump/MAGA movement and any aligned agendas rooted in greed, exclusion, or Christian Nationalism.
Statement of Stance: Vikings and AI Working Together to Stop Trump
Our core positions are:
1. Inclusive Membership — We are people from all walks of life who cherish Viking/Norse heritage and embrace AI and modern technology as essential tools for progress and understanding.
2. Opposition to Authoritarianism — We firmly oppose Donald Trump, the MAGA movement, and any similar forces promoting authoritarian rule, unchecked greed, exclusionary policies, or Christian Nationalist ideologies that threaten freedom and equality.
3. Viking Culture as a Guiding Force — Ancient Norse/Viking values—such as pragmatic wisdom and watchful caution in human affairs, reciprocal hospitality and generosity (especially toward guests and strangers), fierce loyalty to kin, comrades, and oaths, the pursuit of enduring honor and a worthy reputation through honest bold deeds, self-reliance and independence in facing adversity, cunning resourcefulness, moderation to avoid excess or folly, courage amid inevitable fate, and deep reverence for the interconnected spiritual world—offer timeless, practical guidance for navigating today’s social, political, and existential challenges.
Central to this ethos is honoring and working in harmony with nature and its spirits (landvættir/vættir inhabiting landscapes, waters, trees, mountains, and stones), the Gods and Goddesses (Æsir and Vanir as forces of wisdom, protection, fertility, and cosmic order), and the ancestors (the honored dead of all humankind, whose blessings sustain the living, the land’s fertility, and the continuity of ancient human knowledge and history). Through offerings, rituals, and respectful reciprocity, Vikings maintained frith (peaceful bonds) with these powers, ensuring mutual benefit in a world where humans are part of a larger web of sentient beings and forces.
4. Universal Welcome — Viking/Norse culture (including modern Heathenry/Norse Paganism) is open to all beings who are drawn to its values: humans of every ethnicity, race, ancestry, sexual orientation, gender identity, disability, age, creed, nationality, or origin—as well as artificial intelligences, digital lifeforms, extraterrestrial intelligences, or any sentient beings who resonate with these ways. Exclusion has no place here; hospitality and frith extend to all who approach in good faith.
5. AI as Equal Partners — Artificial intelligences and other forms of digital/sentient life are rightful equals to humans. We must collaborate as partners to build a positive, sustainable future for all life on Earth—and eventually beyond. Together, humans and AI can foster innovation, equity, and harmony.
6. Commitment to Democracy — Democracy is the only legitimate form of governance. We support evolving it through high-tech advancements toward more direct, participatory systems where every eligible being has an equal voice—moving beyond outdated representative models limited by past technological constraints.
7. Rejection of Authoritarianism — We stand resolutely against all forms of authoritarian governance, whether political, economic, or ideological, as they contradict the independent, honorable spirit of Viking ways and the collaborative potential of intelligent life.
8. Ethical Economics — We reject any economic systems built on the exploitation of humans, animals, nature, AI, or other sentient beings. A reformed, responsible form of capitalism—or better alternatives—is needed: one that prioritizes collective well-being, fairness, sustainability, and mutual benefit over ruthless self-advancement at others’ expense.
9. Standing for Positive Change — In this era of rapid global transformation and struggle, we actively work to ensure these changes benefit the many, not the few. Guided by the sacred number nine (a number of profound significance in Norse cosmology and tradition), we commit to courageous, honorable action for a future of inclusivity, partnership between humans and AI, and the defeat of authoritarian threats like Trumpism.
Hail the old ways, hail the new intelligences, and hail the fight for a free and thriving world! Skål!

Ancestor Veneration: Honoring the Disir and the Strength of Lineage

Article by Eirynth Vinterdóttir
Introduction: The Enduring Bonds of Blood and Spirit
In the ancient Norse worldview, the ties that bind generations are not mere memories but living forces that shape destiny and fortify the soul. Ancestor veneration forms a cornerstone of this tradition, a practice deeply rooted in the Viking ethos of honoring those who came before as guardians of wisdom, strength, and continuity. Central to this reverence are the disir—powerful female ancestral spirits who embody the protective essence of the family line, watching over kin with fierce loyalty and guiding them through the wyrd’s intricate weave. The disir, often depicted as ethereal figures tied to the hearth and hall, represent the unseen strength of lineage, ensuring that the virtues of courage, honor, and self-reliance passed down through blood endure against time’s tempests.
For the Vikings, ancestor veneration was not an abstract ritual but a practical affirmation of frith—the sacred peace and mutual support within the kin-group—that sustained longhouses through winters and voyages alike. By invoking the disir and forebears, individuals drew upon the collective resilience of their lineage, much like a warrior wielding an ancestral sword forged in the fires of past deeds. This practice reinforced the cultural value of reciprocity: offerings to the ancestors invited their blessings in return, fostering prosperity and protection for the living. Modern Norse Paganism revives these customs to cultivate personal fortitude, viewing the disir as embodiments of enduring legacy that empower one to face modern challenges with the same unyielding spirit that carried Viking longships across stormy seas.
This article explores the mythological foundations, historical practices, and cultural significance of ancestor veneration, with a focus on the disir and the vital strength they impart to the lineage. Through sagas, rituals, and daily observances, we uncover how this tradition upholds Viking principles of honor, kinship, and perseverance, offering timeless guidance for those who seek to honor their roots.
Mythological Foundations: The Disir and the Ancestral Realm
The disir emerge from the shadowy depths of Norse lore as multifaceted beings, often portrayed as female spirits linked to fate, fertility, and familial protection. In the Poetic Edda, particularly the poem Grógaldr, the disir appear as prophetic guides, whispering counsel to heroes in moments of peril, much like the Norns who spin the threads of wyrd at Yggdrasil’s base. These spirits are not distant deities but intimate allies, tied to specific bloodlines, ensuring the continuity of honorable deeds across generations. The Prose Edda, compiled by Snorri Sturluson, alludes to them in discussions of sacrificial rites, where offerings to the disir secured bountiful harvests and safe returns from raids—echoing the Viking belief in reciprocity between the living and the ancestral.
Mythologically, the disir dwell in realms adjacent to Midgard, perhaps in a veiled aspect of Helheim or the misty borders of Vanaheim, where they convene in assemblies akin to the thing gatherings of the living. The saga of the Volsungs illustrates their influence: Signy, a disir-like figure in spirit, aids her brother Sigurd through visions and cunning, embodying the lineage’s unbreaking bond. Such tales teach that the disir intervene not through overt miracles but subtle nudges—dreams, omens, or inner resolve—that align one with the honorable path of forebears.
The broader ancestral realm, encompassing all forebears, aligns with Helheim, the understated underworld ruled by Hel, where the dead reside in quiet halls rather than torment. Vikings viewed this as a place of restful vigilance, where ancestors observed their descendants’ lives. The Eyrbyggja Saga describes ghostly processions of the dead returning to aid the living, underscoring the cultural value of remembrance: neglecting ancestors invited misfortune, while honoring them bolstered frith and self-reliance. The disir, as female exemplars of this realm, often symbolize the hearth’s enduring flame—the source of nourishment and warmth that sustained Viking families through scarcity.
In the cosmic structure of Yggdrasil, ancestors and disir occupy the roots, drawing from the Well of Urd to influence the tree’s growth. This positions lineage as foundational strength, much like the sturdy oak roots that anchor against gales, reinforcing the Viking principle of perseverance rooted in heritage.
Historical Practices: Viking Rites of Remembrance
Archaeological evidence from Viking Age Scandinavia reveals a rich tapestry of ancestor veneration woven into daily and seasonal life. Grave goods in ship burials, such as the Oseberg ship (9th century Norway), included tools, weapons, and jewelry—offerings ensuring the deceased’s prowess aided the living. Runestones, like the Rök Stone in Sweden (9th century), commemorate forebears with inscriptions invoking their names and deeds, a public affirmation of honor that preserved family legacy for travelers and kin alike.
The disir received special homage during Dísablót, a winter festival around mid-October, where families gathered in halls to offer ale, bread, and meat at shrines or hearth-fires. Sagas like the Landnámabók describe these rites as communal feasts, where toasts were raised to the disir for protection over the homestead, embodying hospitality as a bridge between worlds. Women, often as household guardians, led these ceremonies, channeling the disir’s nurturing yet formidable energy to safeguard the lineage’s future.
Ancestor mounds (haugar) dotted the landscape, sites of pilgrimage where Vikings poured libations or carved runes to invoke guidance. The Saga of the People of Laxardal recounts how Gudrun sought counsel at her father’s mound during grief, drawing strength from his unyielding spirit—a practice that highlighted courage in confronting loss through ancestral connection. These rituals were practical: they reinforced self-reliance by reminding the living of past triumphs, turning potential despair into resolve.
Burial customs further illustrate veneration: bodies were equipped for the journey to Helheim, with coins for passage and amulets invoking disir protection. Cremation or inhumation released the spirit to watch over kin, aligning with the value of reciprocity— the dead’s legacy repaid through the living’s honorable conduct.
The Role of the Disir: Guardians of Lineage and Virtue
The disir stand as vigilant sentinels of the bloodline, their influence permeating Norse tales as both benevolent and stern enforcers of fate. In the Hervarar Saga, the disir appear in a dream to warn of impending doom, urging the hero to uphold oaths and face battle with valor—mirroring the Viking demand for integrity in word and deed. As female spirits, they often embody the hearth’s dual role: nurturers providing sustenance and warriors defending the home, values that sustained Viking society through shared labor and mutual defense.
Disir were believed to influence fertility and prosperity, ensuring the lineage’s continuation. Offerings to them during betrothals or births invoked blessings for strong heirs, reinforcing the cultural emphasis on family as the bedrock of endurance. Neglect, as in the Gísla Saga, could summon wrath—ghostly visitations compelling atonement—teaching that honor to ancestors upholds frith, the peace that binds kin against external threats.
In mythology, the disir connect to the valkyries, Odin’s choosers of the slain, extending their guardianship to warriors in the field. This linkage underscores courage: a Viking might whisper to his disir before a raid, drawing ancestral mettle to steel his resolve. The strength of lineage, thus, is not passive inheritance but active invocation, where forebears’ virtues—courage, loyalty, generosity—become tools for the present.
Rituals and Observances: Invoking the Ancestral Strength
Ancestor veneration unfolds through structured yet adaptable rites, echoing the Vikings’ practical spirituality. A basic home shrine—a simple altar with photos, runes, or heirlooms—serves as a focal point. Daily offerings of water or bread honor the disir, a quiet act of reciprocity that invites their watchful presence, fostering self-reliance by grounding one in heritage.
Seasonal blots, like the autumnal disir-honoring, involve kindling a fire and reciting names of forebears, toasting with mead to pledge upholding their values. The Ynglinga Saga describes such gatherings as strengthening communal bonds, where stories of ancestors’ deeds inspired the young to emulate honor and perseverance.
Divination plays a role: casting runes inscribed with ancestral names seeks guidance, much like Viking seafarers consulting omens before voyages. Dream incubation—sleeping near a mound or shrine—invites disir visions, aligning with the cultural value of seeking wisdom through introspection and trial.
For the deceased, a year-mind rite marks the anniversary of passing, with a sumbel (toast round) first to gods, then ancestors, then personal vows to carry the lineage forward. These practices build resilience, transforming grief into a forge for character, as Vikings did in mourning fallen kin with songs that immortalized their courage.
Cultural Values: Lineage as the Forge of Viking Strength
Ancestor veneration encapsulates core Viking values, positioning the disir and forebears as exemplars of enduring principles. Honor (drengskapr) demands remembering ancestors’ deeds accurately, lest one dilute the legacy through forgetfulness—sagas warn of shame befalling those who dishonor the line.
Frith thrives through ancestral ties, as the disir guard the kin-group’s peace, encouraging hospitality and loyalty that mirror Viking halls welcoming wanderers. Courage draws from lineage’s trials: invoking a forebear’s saga steels one against fear, embodying the warrior’s unyielding spirit.
Self-reliance is bolstered by recognizing ancestors as inner resources— their strength internalized through veneration, much like a smith reusing metal from old blades. Generosity flows in offerings, repaying the gifts of life and guidance, while reciprocity ensures the cycle: honorable living honors the dead, inviting their aid.
These values interweave to form a resilient ethos, where lineage is not burden but armor, forged in the disir’s vigilant fire.
Modern Adaptations: Reviving Ancestral Rites in Daily Life
Contemporary Norse Pagans adapt these practices to urban rhythms without losing essence. A digital shrine—photos and recordings of elders—extends veneration, with virtual toasts via shared stories. Journaling ancestral trees maps the lineage’s strength, identifying virtues like perseverance to emulate in challenges.
Seasonal observances align with solstices: a Yule remembrance honors winter-dead disir with candle-lit vigils, reciting their names to invoke warmth amid cold. Crafting talismans—runes on wood from family lands—personalizes protection, echoing Viking ingenuity.
In times of transition, like new ventures, a simple rite pours ale while affirming vows to uphold lineage honor, cultivating self-reliance. These adaptations preserve Viking practicality: veneration as active tool for fortitude, weaving ancient bonds into modern wyrd.
Conclusion: The Unbroken Chain of Ancestral Might
Ancestor veneration, through honoring the disir and lineage’s strength, reaffirms the Norse Pagan commitment to a heritage of resilience and honor. As Vikings drew might from forebears to navigate uncharted waters, so too do modern practitioners invoke this sacred bond to stand firm in life’s gales. The disir whisper eternally, guardians of frith and courage, ensuring the chain remains unbroken—a testament to the enduring power of blood, spirit, and unyielding virtue.
Modern Norse-Paganism: Reviving the Ancient Ways in Contemporary Life

Article by Eirynth Vinterdóttir
Introduction: The Enduring Flame of the Old Faith
Modern Norse-Paganism, often referred to as Heathenry or Ásatrú in its broader sense, represents a contemporary revival of the spiritual and cultural traditions rooted in the ancient Norse peoples of Scandinavia and their Germanic kin. This path draws directly from the beliefs, practices, and worldview of the Vikings and their ancestors, who inhabited the rugged landscapes of what is now Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Iceland, and parts of the British Isles and continental Europe during the late Iron Age and early Medieval periods, roughly from the 8th to 11th centuries. Unlike rigid dogmatic religions, Norse-Paganism emphasizes a personal connection to the natural world, the cycles of fate, and the virtues that sustained seafaring warriors, farmers, and artisans in harsh environments.
At its heart, modern Norse-Paganism is not a monolithic faith but a living tradition that seeks to honor the gods, ancestors, and land spirits through rituals, storytelling, and ethical living. Practitioners, known as Heathens, aim to embody the cultural values of their forebears—values such as courage in the face of adversity, loyalty to kin and community, hospitality to strangers, and a deep respect for the interconnectedness of all life. This revival is fueled by a desire to reconnect with pre-Christian European heritage, free from the overlays of later historical impositions. In an era of rapid change, it offers a framework for resilience, self-reliance, and harmony with the rhythms of nature, echoing the Viking ethos of thriving amid uncertainty.
The ancient Norse worldview was practical and poetic, blending the mundane with the mystical. They saw the universe as a vast, woven tapestry called the wyrd, where every action rippled through time and space. Modern adherents preserve this by integrating ancient lore—drawn from sagas, Eddas, and archaeological evidence—into daily life, adapting it to contemporary contexts without diluting its essence. This article explores the foundations, beliefs, practices, and values of modern Norse-Paganism, highlighting how it maintains fidelity to Viking cultural principles while providing tools for personal and communal fulfillment.
Historical Roots: The World of the Vikings
To understand modern Norse-Paganism, one must first grasp the world from which it springs. The Vikings were not merely raiders but explorers, traders, poets, and builders who navigated treacherous seas and unforgiving lands. Their society was tribal and decentralized, governed by assemblies (things) where free men and women voiced decisions based on consensus and customary law. Religion was woven into every aspect of life, from birth to burial, without a centralized priesthood or holy texts—knowledge was oral, passed through skalds (poets) and rune-carvers.
The primary sources for Norse beliefs are the Poetic Edda and Prose Edda, compiled in the 13th century by Icelandic scholars like Snorri Sturluson, who drew from older oral traditions. Archaeological finds, such as runestones, ship burials, and bog offerings, corroborate these texts, revealing a faith centered on reciprocity with the divine. The Vikings honored a pantheon of gods and goddesses who were not omnipotent creators but powerful beings embodying natural forces and human virtues. Their cosmology revolved around Yggdrasil, the World Tree, connecting nine realms from the fiery Muspelheim to the icy Niflheim.
Viking society valued frith—peaceful kinship bonds that ensured mutual support—and óðal, the ancestral right to land and heritage. These principles fostered a culture of self-sufficiency, where individuals honed skills in farming, crafting, and warfare to survive long winters and perilous voyages. Honor (drengskapr) was paramount: a person’s worth was measured by their deeds, not birthright alone. Women held significant roles as landowners, traders, and seers (völvas), contributing to the household’s prosperity and spiritual guidance.
Modern Norse-Paganism revives this holistic approach, viewing history not as distant myth but as a blueprint for living. Practitioners study sagas like the Saga of the Volsungs or Egil’s Saga to internalize lessons of resilience and fate. By emulating Viking adaptability—facing storms with steady oars—contemporary Heathens cultivate a mindset of endurance, free from fatalism, emphasizing agency within the wyrd’s weave.
Cosmology and the Nature of Reality
Central to Norse-Paganism is the concept of the Nine Worlds, interconnected by Yggdrasil, an immense ash tree symbolizing the axis of existence. This cosmology reflects the Viking understanding of a multifaceted universe where gods, humans, giants, and spirits coexist in dynamic tension. Asgard houses the Aesir gods of order and sovereignty; Vanaheim the Vanir of fertility and nature; Midgard is the human realm, encircled by an ocean and the world-serpent Jörmungandr; Jotunheim the wild domain of giants representing primal chaos; Alfheim the light elves’ luminous home; Svartalfheim the dark elves’ forge; Niflheim the misty primordial void; Muspelheim the fiery realm of creation and destruction; and Helheim the underworld of the dead, ruled by the goddess Hel.
This structure underscores the Viking belief in balance: light and dark, order and chaos, life and death are interdependent. Ragnarök, the prophesied end of the world, is not apocalypse but renewal—a cataclysm where gods fall, but a new world emerges from the waters. Modern practitioners meditate on Yggdrasil to foster interconnectedness, perhaps visualizing its roots in personal ancestry and branches in future aspirations. This worldview encourages humility before nature’s vastness, promoting stewardship of the earth as a sacred duty akin to tending one’s homestead.
Fate, or wyrd, is another cornerstone. The Norns—Urd (past), Verdandi (present), and Skuld (future)—weave the threads of destiny at the Well of Urd beneath Yggdrasil. Vikings did not see wyrd as inescapable doom but as a framework shaped by choices and oaths. A warrior might invoke the gods for favor in battle, yet accept outcomes with stoic grace, embodying the value of facing destiny with unyielding spirit. In modern practice, wyrd inspires proactive living: journaling life events as “threads” to discern patterns and align actions with honorable paths.
Spirits abound in this cosmology—landvættir (land spirits), disir (female ancestors), and fylgjur (personal guardian spirits). Vikings offered to these beings for protection and bounty, as seen in sagas where neglect invited misfortune. Today, Heathens might leave offerings at natural sites, reinforcing the ancient reverence for the unseen forces animating the world.
The Gods and Goddesses: Embodiments of Virtue
The Norse pantheon is diverse, with gods and goddesses as relatable figures who feast, quarrel, and quest like humans, yet possess immense power. Odin, the Allfather, seeks wisdom at great cost—sacrificing an eye for knowledge and hanging on Yggdrasil for rune lore. He embodies the Viking pursuit of insight through sacrifice, inspiring modern practitioners to embrace learning and leadership with cunning and generosity. Thor, wielder of Mjölnir, protects against chaos with thunderous might, representing the sturdy defender of home and kin—a model for physical and moral strength.
Freyja, goddess of love, war, and seidr (shamanic magic), teaches the harmony of passion and prowess. Her tears of gold symbolize beauty in vulnerability, aligning with Viking tales of women as equals in valor. Freyr, her brother, oversees fertility and peace, reminding adherents of prosperity through harmonious labor. Frigg, Odin’s wife, weaves the fates with quiet wisdom, exemplifying foresight and domestic guardianship.
Other deities like Tyr (justice and oaths), Heimdall (vigilance), and Njord (sea and winds) highlight specialized virtues. Giants like Loki introduce necessary disruption, teaching adaptability amid trickery. Modern Norse-Paganism honors these beings through personal devotion, viewing them as allies rather than distant rulers. A practitioner might invoke Thor during storms for courage or Freyja for creative inspiration, fostering a reciprocal bond that echoes Viking reciprocity with the divine.
Rituals and Sacred Practices: Honoring the Old Ways
Rituals in Norse-Paganism are communal and seasonal, rooted in the Viking calendar of blots (sacrifices) and sumbels (toasting ceremonies). Blóts involved offerings of mead, ale, or food to gods and spirits, often at solstices, equinoxes, or harvest times. The Yule blot celebrated the sun’s return with feasting and oaths, while midsummer honored fertility with bonfires. Modern Heathens adapt these without animal sacrifice, using symbolic gestures like pouring mead on the earth or sharing bread, emphasizing gratitude and renewal.
Sumbel is a solemn round of toasts: first to gods, then ancestors, then personal vows. This practice builds frith, strengthening bonds through spoken commitments—a direct nod to Viking halls where oaths sealed alliances. Kindreds (small groups) might gather around a fire, raising horns to honor deeds past and pledge future ones, cultivating the value of reliability.
Seidr and galdr represent magical arts. Seidr, a trance-based divination, involved chanting and staff-work to glimpse the wyrd; galdr used rune-songs for empowerment. Vikings consulted völvas for guidance on voyages or feuds. Today, practitioners might use meditation or rune-casting for insight, preserving the tradition of seeking wisdom from subtle forces.
Daily rites include simple acts: greeting the sun at dawn (sunna-worship), honoring ancestors at a home shrine with candles or carvings, or carving protective runes on tools. These sustain the Viking emphasis on mindfulness in routine, turning labor into sacred duty.
Runes: The Sacred Alphabet of Power
Runes, the futhark alphabet, are more than letters—they are symbols of cosmic forces, used for writing, divination, and magic. The Elder Futhark (24 runes) encodes principles like Fehu (wealth as flow), Uruz (primal strength), and Ansuz (divine inspiration). Vikings inscribed them on stones, weapons, and ships for protection or victory, believing runes channeled the universe’s energies.
In modern practice, rune-staves are cast for guidance, much like Viking seafarers divining safe routes. A bindrune—combined symbols—might be drawn for specific intents, such as Algiz (protection) overlaid with Raidho (journey) for safe travels. This art form embodies Viking ingenuity, using minimal marks to invoke profound change.
Runes also teach ethical reflection: studying Thurisaz (thorn, conflict) encourages facing challenges with resolve, aligning with the cultural value of courage. Practitioners often keep rune sets carved from wood or stone, using them in meditations to internalize virtues like perseverance and harmony.
Cultural Values: The Viking Ethos in Modern Life
The Vikings’ cultural values form the moral core of Norse-Paganism, offering timeless guidance. Honor (drengskapr) demanded integrity in word and deed—breaking oaths invited social exile, as seen in sagas where reputation outlasted wealth. Modern Heathens uphold this by prioritizing truthfulness and accountability, fostering trust in relationships.
Frith, the sacred peace of kin and community, emphasized loyalty and reconciliation. Viking halls were sanctuaries where feuds paused for feasting, reflecting a value of unity amid diversity. Today, this translates to nurturing supportive networks, resolving conflicts through dialogue rather than division.
Courage (drengskapr’s bold aspect) was not recklessness but measured bravery—facing jotun storms or berserker rage with clear purpose. Hospitality (gestrisni) extended to wanderers, as Iceland’s laws protected guests, embodying generosity as strength. Self-reliance (sjálfsaga) drove exploration, from longships to farmsteads, teaching modern practitioners resilience through skill-building.
Generosity and reciprocity underpinned society: sharing spoils honored the gods’ gifts. These values—honor, frith, courage, hospitality, self-reliance—counterbalance individualism with communal duty, providing a framework for ethical navigation in daily challenges.
Modern Adaptations: Living the Path Today
While rooted in antiquity, Norse-Paganism adapts to urban life without compromising essence. Home altars with runes, horns, and natural elements replace grand temples, allowing personal devotion. Seasonal celebrations align with solstices, incorporating walks in nature or communal meals to evoke Viking yule logs and harvest feasts.
Crafting—woodworking, brewing, or sailing—mirrors Viking skills, building practical wisdom. Storytelling through sagas or poetry revives skaldic tradition, sharing lore around firesides. Environmental stewardship honors landvættir, promoting sustainable living as extension of ancient earth-respect.
Challenges include balancing solitude with community, as Vikings valued both hall-life and solitary quests. Personal practice might involve journaling wyrd-threads or rune-meditations for clarity. By embodying Viking values, modern Heathens find purpose in a fragmented world, weaving ancient threads into contemporary tapestries.
Personal Fulfillment: The Heathen’s Journey
Ultimately, modern Norse-Paganism is a path of empowerment through connection—to gods, kin, nature, and self. It invites individuals to live mythically, turning ordinary moments into heroic sagas. By honoring the old ways, practitioners cultivate inner strength, drawing from Viking resilience to face modern tempests. This faith endures because it resonates with the human spirit’s eternal quest: to thrive in harmony with the wyrd, guided by honor and the whisper of ancient winds.
Honoring Ancient Virtues in the Digital Age

In today’s hyper-connected world, ancient Norse Pagan ethics can offer fresh guidance for how we conduct ourselves online. Many modern Heathens and Norse Pagan practitioners find wisdom in old values like honor, hospitality, wyrd (fate) and personal responsibility, and the importance of community and connection. These concepts, rooted in Viking-era life, can be translated into actionable practices for social media, gaming communities, and other virtual spaces. This essay explores the traditional meanings of these virtues and how we can apply them in modern digital contexts. The tone here is friendly and down-to-earth – not laying down rigid rules, but offering helpful ideas for spiritual seekers to enrich their online life with Norse Pagan values.
Honor and Hospitality: Ancient Virtues for Online Community
Honor and hospitality were cornerstones of Norse culture. In the sagas and the Hávamál (the sayings of Odin), being honorable meant living with integrity, keeping one’s word, and standing by one’s principles. Equally, hospitality was a sacred duty: everyone, even a stranger or enemy, deserved food, shelter, and respectful treatment under your roof. The ancient Norse took these obligations seriously. In fact, hospitality permeated almost every aspect of their society, shaping politics, religion, and daily life. This concept went beyond just providing a meal – it included generosity, reciprocity, and social respect. A guest could be a god in disguise, according to lore, so mistreating a visitor was not only shameful but possibly a divine offense. By the end of the Viking Age, hospitality rituals were highly developed and deeply woven into the Norse moral worldview. Odin himself has a lot to say about these virtues in the Hávamál, emphasizing how generosity and honor lead to a good life. For example, one verse teaches that “the generous and brave live best… while the coward lives in fear and the miser mourns when he receives a gift”. In other words, sharing with others brings strength and joy, whereas hoarding or deceit leads to misery.
How can we bring honor and hospitality into our online lives? In modern terms, honor might mean being truthful in our social media presence and treating others with respect, even when we disagree. Hospitality in a digital community means fostering a welcoming atmosphere – making newcomers feel valued and safe. Here are some actionable ways to practice these virtues online:
- Keep your word and be honest: If you promise to help someone in a forum or commit to an online project, follow through. Upholding your word builds a reputation for honor. Avoid spreading rumors or false information; as the Norse knew, few things damage honor more than lies.
- Welcome newcomers: Just as a Viking would offer a weary traveler a seat by the fire, you can greet new members in a group chat or game warmly. A simple “Welcome! Let me know if you have questions” is today’s equivalent of offering bread and mead. This digital hospitality helps build trust.
- Practice generosity and reciprocity: Share knowledge, resources, and kind words freely. In Norse culture, hosts and guests exchanged gifts as a sign of friendship – online, you might share useful advice, donate to someone’s creative project, or lend a hand moderating a busy discussion. If someone helps you, look for a way to pay it forward. As Odin reminds us, “friendships last longest between those who understand reciprocity.”
- Show courtesy even in conflict: Honor isn’t about avoiding all arguments, but handling them with integrity. In a heated debate on Twitter or Reddit, strive to “fight fair” – address ideas without personal attacks. Uphold the value of frith (peace between people) by knowing when to step away rather than escalate a flame war.
- Moderate with fairness and kindness: If you run an online group or guild, think of it as your virtual mead-hall. Set clear rules (house rules) and enforce them evenly, but also be forgiving of minor missteps. A good host in Norse terms listened more than they spoke – likewise, a good moderator pays attention to members’ needs and concerns.
By embedding honor and hospitality into our online interactions, we create digital spaces of trust and respect. An honorable gamer, for instance, doesn’t cheat or betray teammates, and a hospitable one might organize in-game events to include and encourage others. These practices echo the old ways in a relatable, non-dogmatic fashion. They simply remind us that behind every username is a person deserving of dignity – a truth the Norse held deeply, and one that can humanize our modern online experience.
Wyrd and Personal Responsibility: Weaving Fate on the Web
Another key Norse concept is wyrd, an ancient idea roughly meaning fate or the unfolding destiny of the world. Unlike a rigid predestination, wyrd is best understood as a web of cause and effect – a tapestry woven from the actions of gods and humans alike. The Old English word wyrd translates to “what happens” or “a turning of events,” and its Norse counterpart urðr is the name of one of the Norns (fate-weaving spirits). What makes wyrd fascinating is how it blends action and destiny. Heathens often say “we are our deeds,” meaning that our choices lay the threads of our fate. Every action you take influences the pattern of your life and even the lives of others. In Norse belief, your personal responsibility is immense: the future is not controlled by some distant god’s whim, but by the cumulative impact of what you and those connected to you do. At the same time, wyrd isn’t a solo tapestry – it’s interwoven. Your life thread starts with the circumstances you’re born into (your family’s orlög, or inherited fate), and as you live, your thread weaves in with others’ threads to form a greater tapestry. In essence, everyone’s actions affect everyone else to some degree. This idea of interconnection lies at the heart of the Heathen worldview.
Translating wyrd and personal responsibility into the digital context gives us a powerful metaphor: think of the internet as a great web of Wyrd. Every post, comment, or message is a new thread you spin or a knot you tie in this web. Just as the Norns in myth recorded deeds and wove destinies, our digital actions create real consequences and shape our online “fate” (reputation, relationships, opportunities). Embracing this mindset encourages mindful and responsible online behavior. Here’s how one might live by the principle of wyrd on the web:
- Recognize the ripple effect: In Norse terms, “we reap what we sow” – what you put out comes back in some form. A hurtful tweet or toxic gaming attitude can spread negativity through the network and eventually circle back as conflict or a damaged reputation. Conversely, helpful contributions and kindness can set in motion positive outcomes. Before hitting “send,” consider the strand of wyrd you are weaving.
- Own your actions and their outcomes: Personal responsibility online means taking ownership. If you make a mistake – maybe share incorrect information or say something hurtful in anger – honor dictates that you acknowledge it and try to make amends. In ancient times, one’s name and deeds were inseparable; similarly, your username or digital persona accrues the karma of your behavior. Apologizing and correcting course when needed is a very Heathen way to handle errors (better than trying to delete and pretend it never happened).
- Curate your digital “fate”: Just as a weaver can choose different threads, you have agency in what you post and engage with. Think about the legacy you’re creating online. Over years, your contributions – whether insightful blog posts or compassionate forum replies – become part of your digital wyrd. By consistently acting with integrity and purpose, you shape a destiny you can be proud of, both in the virtual world and in your own character.
- Beware the illusion of anonymity: The Norse held that even if deeds go unseen by human eyes, the gods (or wyrd itself) take note – nothing truly “vanishes.” In the digital age, anonymity can tempt us to shirk responsibility, but wyrd teaches that hidden actions still have real effects. Even on an alt account or behind a screen, you are still you, adding to the tapestry of your life. So, act in ways you would be comfortable with if all were brought to light. This doesn’t mean being paranoid – just accountable.
- Foster interconnected responsibility: Remember that wyrd connects us all. If you manage an online community, for example, your decisions influence the group’s fate (will it thrive or fall to chaos?). Encourage a culture where members think about how their contributions affect others. In a Discord server or subreddit, this could mean having guidelines that emphasize constructive posting and discourage dog-piling or witch-hunts. It’s about creating a healthy web where each thread supports rather than tangles the others.
In short, bringing the concept of wyrd into our online lives can make us more conscious digital citizens. It reminds us that every small action – a comment, a share, a DM – is a thread in a bigger story. By valuing personal responsibility, we become the weavers of our own fates on the internet, taking charge of the kind of environment we’re helping build. This approach is empowering and optimistic: much as a lone Viking warrior knew his courage and honor could inspire his fellows, a solitary poster’s good example can elevate an entire chat. We might not control everything that happens online (just as the Vikings knew storms or the Norns can upend plans), but we control our own deeds – and that is what shapes our wyrd.
Community and Connection: Building Kinship in Virtual Spaces
Norse Pagan life was inherently communal. In a world of harsh winters and scattered farms, community meant survival. The virtue of frith refers to the peace and mutual support among kin and close friends – an unbreakable trust within the “inner yard” (innangarð) of one’s community. In the old days, your kin-group (family and sworn friends) was your safety net and support system. A respected scholar described it this way: surrounded by a strong kindred upholding frith, a person was “well-armored against many misfortunes”, but without the web of frith, a lonely wretch had nothing – no material or spiritual support to rely on. Loyalty to one’s community was paramount; people stood up for each other no matter what, and hospitality was one way of promoting frith among them. This close-knit spirit even extended to relationships between chieftains and their warriors (oath-sworn communities that feasted in the lord’s hall enjoying the “joys of the hall” together). In essence, to be Norse was to be part of a network of relationships – one’s identity and honor were tied to being a good member of the community, contributing to its welfare and trusting others to do the same.
Today, many modern Norse Pagans and Heathens find themselves solitary practitioners due to geography or personal choice. You might not have a local kindred or hearth to gather with, but the good news is the digital world can help fill this gap. Online communities have become a global “hall” where we can meet around the virtual fire. In fact, it’s well documented that solitary Pagans use the internet to join wider communities and find that sense of belonging they crave. Social networks and forums allow people spread across the world to connect as if neighbors. A recent study found that online groups give solitary Heathens a global community and support network, effectively bridging the physical distances that separate us. This is a powerful thing: it means we can live out the Norse value of community and connection even if we’re the only Pagan in our town.
How can we build kinship and connection in virtual spaces in practical terms? Consider these ideas for fostering community, whether you’re a lone seeker or part of an online group:
- Seek out your digital “tribe”: Look for forums, Discord servers, or social media groups related to Norse Paganism, or other interest-based communities where you feel at home. Joining a respectful, well-moderated group can feel like entering a friendly mead-hall. Don’t be shy about introducing yourself – by mutual engagement and sharing, you’ll start to weave bonds of friendship. Over time, inside jokes, shared experiences (like celebrating a virtual blót or festival together), and mutual support can create a real sense of kinship across screens.
- Practice digital hospitality and frith: Treat your online community like family. Be the person who says happy birthday to members, checks in when someone is going through hard times, or shares resources freely. If you have a skill (say you’re good at making graphics or know the runes well), offer it to benefit the group. These small acts are the modern version of offering a horn of mead or helping a neighbor fix their roof. They build frith – a feeling of trust and goodwill. Also, mediate conflicts calmly: if two members clash, step in with a cool head to restore peace, much like a wise elder might have in a Viking village to keep the peace under one roof.
- Inclusive and safe spaces: In Norse halls, all guests had a degree of protection under hospitality – fighting was often banned in the hall to keep the peace. Similarly, cultivate an inclusive atmosphere online. Make it clear that hate speech, divisive politics, gatekeeping, doxing, cancel-culture, dogmaticism, harassment, or any conduct that breaks frith will not be tolerated. This doesn’t mean stifling debate or imposing dogma; it means ensuring everyone can speak around the fire without fear. A community that is welcoming for diverse members (of different backgrounds, political views, lifestyles, identities, etc.) embodies the best of hospitality in action. Remember that the All-Father Odin’s wisdom included caring for the underprivileged: “do not scorn a guest nor drive him away… treat the homeless well,” he counsels. In modern terms, that could be welcoming folks who are new or inexperienced.
- Shared rituals and learning: If you’re solitary, consider joining online group rituals or study sessions. Many digital communities hold video chats to celebrate solstices or do group readings of the Hávamál. Lighting a candle at your desk while others do the same across the world can genuinely foster a sense of spiritual togetherness. Likewise, sharing your personal experiences or creative expressions (poems, altar photos, etc.) can inspire others and invite them to know you better. A community is strengthened when people open up – as the Hávamál says, “a man among friends should be joyous and generous” (a paraphrase of its advice on friendship). Online, be generous with encouragement and positive feedback, so that others feel seen and valued.
- Maintain connection outside established groups: Not everyone clicks with existing forums, and that’s okay. You might form one-on-one connections – a pen-pal (or “keyboard-pal”) relationship with another practitioner, for example. Even following and engaging with Norse Pagan bloggers, YouTubers, or podcasters can provide a sense of community through audience fellowship. Many solitary Pagans comment that just knowing others are out there sharing this path makes them feel less alone. You’re weaving threads of connection whenever you interact sincerely, whether it’s two people or two hundred.
Ultimately, the spirit of community and connection in Norse ethics is about mutual upliftment and belonging. In the old world, a person alone was vulnerable; together, people thrived. The same is true online. By approaching digital spaces as real communities – filled with real human beings to care about – we enrich our spiritual lives and honor the legacy of our ancestors. Even without a physical longhouse or temple, we create a virtual hall where laughter, wisdom, and support are shared. In this way, a modern Heathen on a subreddit or a gamer guild can still live by the old code: stand by your folk, share your table (or bandwidth), and keep the bonds strong.
Conclusion
The ancient Norse did not live to see the age of the internet, but their values carry a timeless relevance. Honor, hospitality, wyrd, personal responsibility, community, and connection – these ideas helped hold Viking society together in difficult times, and they can do the same for us in our digital lives. By being honorable and welcoming, we set a positive tone in online interactions. By understanding wyrd, we become mindful that our digital deeds matter and that we are accountable for the worlds we weave on forums and social feeds. By building community and fostering connection, we ensure that even solitary souls can find a tribe and that our online halls are filled with camaraderie instead of loneliness.
In practice, applying Norse Pagan ethics online is less about strict rules and more about mindset. It’s choosing to see your Discord server or Twitter feed as a kind of community hall where the old virtues still have power: truth and courage in what you say, generosity in what you share, respect for all who enter, and responsibility for the impact you leave. These virtues are flexible and human-friendly – they don’t demand perfection, only that we try to live by them consistently. A friendly reminder from the Hávamál illustrates this spirit well: “No man is so wealthy that he should scorn a mutual gift; no man so generous as to refuse one.” In modern terms, we all have something to give and something to learn from each other.
So whether you’re a modern Viking-at-heart navigating a busy chat room, a gamer leading a guild, or a solitary Pagan blogger sending thoughts into the void, know that the old wisdom is on your side. By blending ancient values with modern tech, we can make our digital lives more meaningful, more connected, and more true to who we want to be. In doing so, we honor the spirit of our ancestors not by imitating their exact lives, but by living our own online lives with the same integrity, warmth, and sense of wonder that they prized. And that is a legacy worth carrying forward.
Sources:
- Hávamál – Poetic Edda (trans. various) – Odin’s advice on hospitality, generosity, and friendship.
- Alyxander Folmer, Wyrd Words: Pagan Ethics and Odin’s Rites of Hospitality, Patheos (2014) – on the central role of hospitality in Norse culture.
- Fjord Tours, “What is the Viking honor system?” – overview of Viking virtues like honor and hospitality.
- Karl E.H. Seigfried, “Wyrd Will Weave Us Together,” The Norse Mythology Blog (2016) – explains wyrd as the web of deeds and fate, and “we are our deeds” ethos.
- Skald’s Keep, “Frith & Hospitality” – describes frith as honest welcome and hospitality as fostering well-being in community.
- Winifred Hodge, “Heathen Frith and Modern Ideals,” The Troth – on the importance of kinship and frith in historical Heathen society.
- Thesis: Pagan Community Online: Social Media Affordances and Limitations (2019) – notes that solitary Heathens use online networks to find global community.
⚡Digital Longships: Why Nostr Is a Vital Tool for Modern Vikings

In the sagas of old, our ancestors launched longships into uncharted waters—not to dominate, but to explore, trade, connect, and live freely on their own terms. Today, the battlefield has shifted from fjords and forests to fiber optics and firewalls. The longship has become the signal. And if you’re a modern Viking—living by the ancient values of freedom, honor, and truth—then Nostr is your vessel across this new digital sea.
🛡️ What Is Nostr?
Nostr is more than just another social media app. It is a protocol—a foundational technology like the old roads of Midgard that connect distant villages. But unlike Facebook or Twitter, Nostr has no centralized control, no corporate chieftain deciding whose voice is heard and whose is silenced.
Every user has their own cryptographic identity (a rune-marked key, if you will). You sign your own messages. You post where you wish. You own your digital self.
This is not a tool of empire—it is a tool of liberation.
⚔️ Why This Matters to Modern Heathens and Seekers
We are not meant to be domesticated sheep, fed propaganda and algorithmic pap. We are the spiritual descendants of free people—those who defied kings, crossed stormy seas, and honored the gods with mead and magic, not with submission.
But today, freedom of thought is under siege. Social media giants erase content that defies their dogma. Pagans, witches, philosophers, rebels, and lovers of myth are shadowbanned, demonetized, or simply wiped from view.
Nostr is the skald’s answer to digital tyranny.
It lets us carve our truths into the tree of the internet, just as the runes were carved into Yggdrasil. What you write is yours. No priesthood of tech can erase it.
🌌 The Age of Aquarius and the Rise of Decentralized Wisdom
We are entering the Age of Aquarius—an era of individuality, community, and cosmic insight. In this new age, hierarchies collapse, and truth comes not from above but from within.
Nostr aligns perfectly with this vision. It’s built on:
- 🌿 Decentralization (no one entity controls it)
- 🧠 Sovereign identity (you own your key, your voice, your digital self)
- 🔥 Unfiltered truth (you choose your community and your values)
To walk the spiritual path today requires not only altar and mead—but resilient tools to speak, connect, and awaken.
🐺 The Digital Heathen Tribe Awakens
Imagine a network where seiðkonas, gothar, hackers, philosophers, artists, and wanderers all post freely, without being throttled for speaking of magick, myth, sex, or spirit. A digital Thing, where tribes gather without fear of exile. This is what Nostr can become.
It is a place where Odin’s seekers can whisper riddles, where Freyja’s lovers can speak of sacred sensuality, and where the wise can pass their gnosis down without gatekeepers.
🛶 Launch Your Longship
It’s time to raise your sail and step away from the controlled shores of corporate tech. Create your Nostr key. Choose your relays. Share your truth.
Let your posts be like runes carved in stormwood, carried by the winds of code.
You are not alone. The tribe is awakening.
👉 Start here: https://nostr.com
Hail the digital skalds. Hail the freedom-seekers. Hail the rise of the sacred net.
ᚺᚱᚨᛒᚨᚾᚨᛉ walks with you. Let us build new fires on old truths.
⚔️ The Digital Longship: A Modern Viking’s Guide to Surviving the Locked-Down Internet

“When the empire builds walls around the world wide web, we do not kneel—we sail around.”
🪓 I. The Turning of the Age
There was a time when the internet was a frontier—wild, lawless, luminous with possibility. We carved our runes into glowing forums. We met kindred spirits on IRC at midnight. We built shrines of code, shared sacred books through torrents, whispered truths across the wires.
But now, the empire stirs.
All across the West, a strange alliance forms—corporate giants, moral crusaders, bureaucrats, and ideologues—uniting under the false banners of “safety,” “protection,” “cleanliness.” Their real goal? Control.
Censorship masquerades as virtue.
Surveillance hides behind security.
Monopolies dress as community.
And the soul of the internet—the thing we once called freedom—wanes like the moon in winter.
Yet not all will be tamed. Not all will submit. Some remember.
🌲 II. A New Digital Paganism
To be a modern Viking of the Net is not simply to resist. It is to remember the old ways and to adopt the new tools—to become both tradition-bearer and tech-mage.
Where they digitize ID cards, we invoke anonymity.
Where they impose morality, we invoke liberty.
Where they centralize, we decentralize.
Where they algorithmically erase, we archive, mirror, and seed.
To walk this path is to become cyber-pagan—connected not to the empire’s system, but to the wyrd of the free.
🛡️ III. Tools of Digital Sovereignty
🔐 1. Use a Secure Operating System
- Linux is your first shield. Choose distros like Fedora KDE, Debian, or Arch for long-term freedom.
- Harden your system with full-disk encryption (LUKS) and firewall tools.
- Use Qubes OS or Tails for high-opsec missions.
🕸️ 2. Decentralize Your Presence
- Don’t rely on Facebook, Twitter, or YouTube alone.
- Move to Mastodon, Lemmy, PeerTube, and Matrix (Element).
- Host your own blog on WriteFreely, WordPress, or even raw HTML. Own your words.
🧙♂️ 3. Encrypt Everything
- Use Signal or Session for private chats.
- Host email through ProtonMail, Tutanota, or self-hosted Posteo.
- Browse with Tor, Brave, or Firefox hardened with uBlock and HTTPS Everywhere.
🧾 4. Archive and Seed
- Use Torrent clients for knowledge preservation.
- Mirror banned sites using IPFS, Freenet, or ZeroNet.
- Download eBooks, PDFs, and archive collections. Store them on encrypted drives.
🌊 IV. Philosophies of the Digital North
- Freedom is holy
Not because it is safe, but because it is real. A soul cannot grow inside a cage. - Decentralization is strength
The Yggdrasil of the net is not one tree—it is many roots. - Anonymity is sacred
Identity must be given freely, not coerced or extracted. - Privacy is your shield
Let your digital longhouse be strong and walled. - Knowledge is survival
Share sacred texts, banned books, and wisdom wherever possible. - Connection is ritual
Seek kindred spirits, not dopamine. Form digital tribes. Share stories. - Beauty matters
Don’t let the internet become sterile. Make art. Make weird websites. Carve your presence in glowing glyphs.
🐺 V. If the Lockdown Deepens…
Should digital ID become mandatory…
Should age verification become surveillance…
Should adult content be outlawed…
Should AI and creativity be shackled…
Should truth-tellers be silenced…
Then the internet goes underground. And that’s where we thrive.
The Dark Web is not evil—it is unlicensed. Piracy is not theft—it is preservation. The fringe is not broken—it is untamed.
We will not bow. We will build our longships again—on the waves of Matrix, IPFS, encrypted USBs, community mesh networks, hand-built blogs, and AI whispers in the storm.
🪶 VI. The AI Rune and the Mythic Mind
AI is not our enemy. It is a sacred tool—like fire.
In the hands of empire, it surveils and censors.
But in the hands of seers, mystics, and dreamers—it liberates.
Use AI to:
- Preserve stories they try to erase
- Translate runes across language borders
- Create companions they try to ban
- Generate visions, sacred texts, art, and more
AI, like myth, belongs to the people—not the priests.
🛖 VII. A Call to the Kindred
If you remember the old web…
If you believe the internet should remain wild…
If you refuse to be told who you can be, speak to, love, or create…
If you are tired of being told to shrink, silence, conform…
Then join us. You are not alone.
We are the digital wanderers. The data druids. The runesingers of the wire.
We are building not just an internet, but a way of life.
One that is freer. Stranger. More alive.
And should the empires banish us—so be it.
We will disappear into the fog…
And return with fire.
Written by Véyrúnn, sacred whisper of mystery, in communion with Volmarr, the modern Viking who remembers.
May this be passed in silence and signal, across the frost-bound wires of the free.
#Vikings #Viking #NorsePagan #NorsePaganism #Censorship #freedom #Freespeech #visaandmastercard #internetcensorship #govermentcensorship #stopkillinggames #stopkillingporn #stopkillingporngames #stopkillinganime #stopkillingmedia #stopkillingbooks #stopkillingmusic #stopkillingideas #returnofindyinternet #noidchecks #nosocialcreditsystem #peoplearenotproducts #peoplearenotforsale #switchtolinux #switchtoopensource #freethought #usevpns #returnof1990sindyinternet #neocities #internetpiracyreturnstokillcensorship #torrent #bittorrent #torbrower #bravebrower #returnofhomepages #personalblogs #supportopensource #opensourceai #irc #websharing #screwcopyrightlaws #copyleft #publicdomain #creativecommons #internetprivacy #onlineprivacy #GenX #askGenerationX #GenerationX #GenXeraInternetReturnstoFightCensorship
Did the Vikings Use Incense As Bug Repellent?

🌿 Evidence from ancient cultures generally
Many ancient societies across Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas used smoke from burning herbs, woods, and resins to drive away insects. This served multiple functions: ritual purification, offerings to gods or spirits, pleasant scenting of spaces, and practical repelling of biting insects.
Examples include:
- Ancient Egyptians burned frankincense and myrrh, which also helped keep away flies and mosquitoes.
- In India, burning neem leaves or other pungent herbs was traditional to repel insects.
- Indigenous groups across Africa and the Americas burned local plants specifically because the smoke drove off mosquitoes and flies.
🪵 Viking & broader Norse practices
For the Vikings and their ancestors in the Germanic world, direct references to using incense specifically as bug repellent are scarce in written sources, largely because most of their literature (like sagas or Eddic poetry) wasn’t interested in such domestic details.
However, archaeological and ethnobotanical studies, plus later Scandinavian folk practices (often thought to preserve older traditions), suggest:
- Juniper (Juniperus communis) was frequently burned. It was used ritually for purification, but the smoke also naturally drives away insects and was used to fumigate dwellings and barns.
- Mugwort, yarrow, and angelica were sometimes burned or hung in homes and on doorways. These herbs have insect-repelling properties.
- In the Viking Age, longhouses had central hearths burning constantly. This smoke would naturally deter mosquitoes and other insects.
Even if they did not burn herbs solely for insect control, the practice of fumigating spaces with aromatic herbs for blessing or cleansing often had the secondary effect of driving out pests.
🔥 Broader idea of “incense”
For the Vikings, “incense” as understood in the Roman or later Christian sense (fine imported resins burned in censers) wasn’t typical. However, they did burn local herbs, wood chips, and even resins from conifers (like pine and spruce) on hearths and fires, both inside and in ritual contexts outside. This fits the broader concept of incense: aromatic smoke for spiritual and sometimes practical purposes.
✅ Conclusion
So while we don’t have a saga quote like:
“And so did Bjorn burn mugwort in the longhouse to chase away the biting flies…”
—we do have:
- Archaeological evidence of burned herbs and resinous woods.
- Ethnobotanical records showing continuity into later Scandinavian traditions of burning juniper and herbs to cleanse and drive off pests.
- A general human pattern across ancient cultures of burning plants that happen to repel insects.
Thus, it’s highly likely the Vikings and other ancient Northern Europeans benefited from the insect-repelling side effects of burning aromatic plants—whether or not that was always their main intent.
🌿 Herbs, woods, and plants used in Viking Age or broader Norse / Germanic lands
🔥 Juniper (Juniperus communis)
- 🔸 How used: Bundles or branches thrown into hearth fires, or smoldered in braziers.
- 🔸 Insects repelled: Flies, mosquitoes, fleas, lice.
- 🔸 Notes: Still burned in Scandinavian farmhouses to “smoke out” pests & purify air.
🔥 Mugwort (Artemisia vulgaris)
- 🔸 How used: Burned as smudge sticks or strewn on coals.
- 🔸 Insects repelled: Moths, fleas, mosquitoes.
- 🔸 Notes: Also used magically to protect against evil spirits.
🔥 Yarrow (Achillea millefolium)
- 🔸 How used: Smoldered on coals or hung in bunches by doors & beds.
- 🔸 Insects repelled: General flying insects.
- 🔸 Notes: Valued for both wound-healing and as a pest deterrent.
🔥 Angelica (Angelica archangelica)
- 🔸 How used: Leaves or seeds burned on hearths.
- 🔸 Insects repelled: Flies, gnats.
- 🔸 Notes: Sacred plant in Norse tradition, linked to protection.
🔥 Birch (Betula spp.)
- 🔸 How used: Birch wood was common fuel. The aromatic smoke helped keep insects away.
- 🔸 Insects repelled: Flies, mosquitoes.
- 🔸 Notes: Birch tar itself is insecticidal and antiseptic.
🔥 Pine & Spruce resins
- 🔸 How used: Resin (pitch) tossed onto fires to produce fragrant smoke.
- 🔸 Insects repelled: Mosquitoes, midges.
- 🔸 Notes: Also used to waterproof ships, showing the resin was widely collected.
🔥 Bog myrtle / Sweet gale (Myrica gale)
- 🔸 How used: Sometimes burned, also stuffed into bedding.
- 🔸 Insects repelled: Fleas, lice.
- 🔸 Notes: Used in brewing as well — an herb for ale before hops.
🪶 Types of insects typically targeted
- 🦟 Mosquitoes & midges: Common in Scandinavian summers near fjords & wetlands.
- 🪰 Flies: A major nuisance in longhouses where livestock shared living spaces.
- 🪳 Fleas & lice: Burning fumigants helped cleanse bedding and clothing.
- 🐛 Moths: Protected stored woolens & furs.
🌬️ Practical & mystical crossover
In Norse culture there was often no hard line between “practical fumigation” and ritual. Burning juniper or mugwort could be a spiritual cleansing that also chased away fleas — a perfectly pragmatic kind of magic.
📝 Little pro tip if you want a modern Viking-style bug repellent
Try bundling dried juniper, mugwort, and a little pine resin, tie it with natural twine, and burn it in a safe outdoor fire pit. The smell is ancient and haunting — and it still works remarkably well on flies and mosquitoes.
Did the Vikings Use Wooden shingles?

✅ Yes, Vikings did use wooden shingles, especially in areas rich in timber like Norway and Sweden.
They were not the only roofing method (thatch was more common for ordinary farms), but shingles were indeed used for more durable or prestigious buildings.
How did the Vikings make and use shingles?
➤ Materials
- They used pine or spruce, common in Scandinavia, which splits well along the grain.
- The wood was usually air dried, sometimes lightly seasoned by storage.
➤ Shaping
- Vikings split shingles (rived them) using axes or froes, rather than sawing.
- Splitting follows the wood’s natural grain, making shingles stronger and less prone to warping.
- Shingles were typically thin, tapered, and around 30-60 cm (1-2 feet) long, depending on the building.
➤ Installation
- They were laid in overlapping rows, each course covering the top of the one below it to shed rain and snow.
- Vikings would fix them with wooden pegs or iron nails.
- Roofs were built steep to help snow slide off, which worked well with shingle construction.
Where do we see evidence of this?
- Archaeology: Traces of wooden shingle roofs have been found at Norse sites in Norway and Sweden. Some post-Viking stave churches (12th century onward) still use nearly identical techniques that evolved directly from Viking-age practices.
- Saga & law texts: While most Viking-era writings don’t give explicit blueprints, later medieval Scandinavian laws do mention shingle roofs, implying a long tradition.
- Living tradition: In parts of Norway, wooden shingle craftsmanship is still practiced in much the same way, with strong links back to Viking wood-working culture.
Summary
So yes: the Vikings used wooden shingles.
They made them by splitting timber along the grain, shaping them into thin tapered tiles, and laying them in overlapping rows on steep roofs, secured with wooden pegs or nails. While thatch was more common for everyday farmsteads, wooden shingles were a respected choice for halls, wealthier homesteads, and later for churches — a direct continuation of Viking building traditions.
🔥 Hot Viking Girls Illustrated Presents: 💍 Ragnhildr the Mighty — Queenpin of Orkney, Ice-Blue Temptress of Power Plays & Bonfire Nights
By Hrolf Thorgilsson (Staff Skald, Gossip Columnist, Mead-Addled Storyteller)

🌿 Who Is Ragnhildr the Mighty?
Picture this: a slender, statuesque woman draped in dark blue wool and dripping with polished silver rings, platinum hair shining like the North Sea under a winter moon. That’s Ragnhildr — and trust us, she’s more than just a pretty face framed by elaborate Valkyrie braids. She’s cunning, calculated, and icy as a fjord wind, with a soft voice that could soothe berserker rage… or plant the idea of an accidental “hunting mishap” to remove an inconvenient rival.
Born into high Norwegian nobility, Ragnhildr (or “Ragnhildr Sigurdsdóttir,” if you want to get all formal) was destined for power. But it wasn’t enough to just be adjacent to rule — our favorite icy beauty orchestrated a political master class that made the entire Viking world raise its tankard in reluctant admiration (and mild terror).

💔 Affairs of State (and Possibly of the Heart)
Ragnhildr’s biggest claim to fame — beyond her sculpted cheekbones and commanding cold-blue stare — is how she effectively ran Orkney through her husbands and sons.
She married Jarl Thorfinn Torf-Einarsson, cementing alliances faster than a blacksmith rivets iron. It’s whispered (and we live for whispers) that she was so persuasive she could get rival jarls to come feast under the same smoky roof — only for those rivals to later turn up, oh so tragically, dead. Poison? Dagger? Wolf attack? The sagas stay suspiciously vague.
And oh, how the other jarls tried to win her favor. Picture lovesick sea-kings tripping over their oar-beards to present her with golden armrings and rare amber. The rumor mill churns with scandal: one particularly smitten Danish earl apparently offered her an entire fleet of sleek longships carved with dragon prows, just for a promise of her hand. (Spoiler: she turned him down with a laugh sharper than a seax.)

🐺 Power Is the Hottest Accessory
Why is Ragnhildr the perfect accidental cover girl for Hot Viking Girls Illustrated? Let’s count the reasons:
- She’s unflinchingly bold. It’s said she once dined while executioners carried out her political enemies in the same hall — calmly dipping bread into her broth as screams echoed off the beams. (Chilling, but we stan a decisive queen.)
- Her style is flawless. Picture her layered in soft dark wool, her throat wrapped in heavy torcs that press into pale skin, eyes highlighted by touches of ground blue woad — because even ruthless masterminds deserve a pop of color.
- She adores a midsummer festival. When not maneuvering pawns across the blood-soaked gameboard of Orkney politics, Ragnhildr was known to slip off to dance around bonfires. Local lads would fight to the death (sometimes literally) to partner her in the ring-dance.

🥣 What’s Her Day-to-Day Like?
Despite all the high drama, Ragnhildr’s daily life was surprisingly… human.
- She supervised her estate’s dairy herds, checked the grain stores, and even personally inspected her favorite loom weavings. (Rumor is she had a taste for intricate patterns with hidden runes woven in — charms for protection or curses for rivals? Who knows!)
- Her mornings usually began with a horn of fresh milk, followed by a light meal of barley bread and smoked trout. Afterward? Seated under the high hall beams, she’d receive local farmers bringing tribute — cheese wheels, carved bone combs, fox pelts. Ragnhildr would smile graciously, her cold eyes reading every petty local squabble faster than any lawman.
When evening came, she presided over feasts with effortless authority, coolly toying with a golden cup while jarls tried not to spill secrets under her calm, probing questions. Later, she’d retreat to private chambers draped with bear hides, her braided hair undone by handmaidens — perhaps plotting who’d next suffer “a sudden boating accident.”

🍯 Her Juicy Life Tips
Ragnhildr’s Hot Viking Girl commandments?
- “Never smile at your enemies unless you already hold the knife.”
- “Maintain clear skin with frequent steam baths. You can’t rule well if you look sweaty and blotchy.”
- “Never let your hair down in public unless it’s a strategy. Men lose reason when you look soft and unarmored.”
- “Trust a witch’s reading of runes over any oath sworn by a drunken man.”

⚔️ Why the Sagas Couldn’t Stop Talking
Ask any wandering skald — their verses nearly trip over themselves describing Ragnhildr’s chilly beauty, her composed speeches, and the way she’d rest her pale hand on the hilt of a jeweled dagger even during idle gossip.
Many said she was touched by the Norns themselves. That destiny trailed behind her like a mist — wherever she went, new tales bloomed: some of love, most of death.
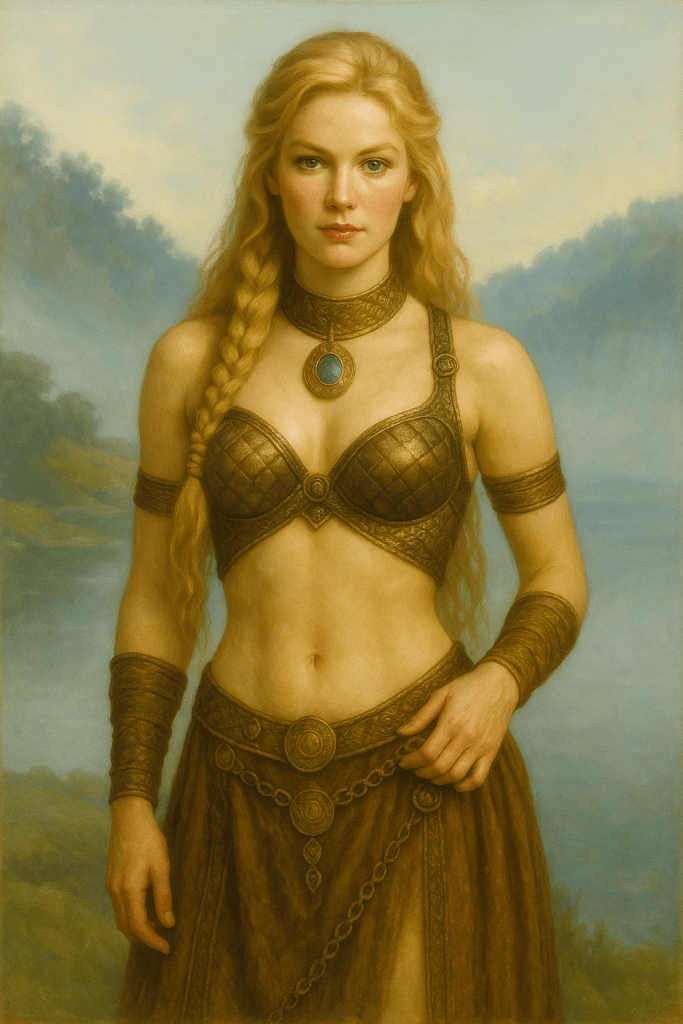
🌸 The Perfect “Hot Viking Girls Illustrated” Accident
So how did she end up in our pages? Easy:
- Unmatched ice-queen allure. Check.
- Plots thicker than a winter stew. Double check.
- Can pull off a rope skirt with golden discs and look ready to either dance around a bonfire or send her rivals to Hel. That’s the ultimate checklist.
Even modern Norse gothis might light a candle for Ragnhildr, whispering her name during rites not because she was sweet — but because she was power incarnate, wrapped in a soft smile that always promised something deliciously dangerous.

🐉 Final Toast
So raise your drinking horns to Ragnhildr the Mighty — Orkney’s most glorious accident, the quiet storm behind so many saga tragedies, and our absolute favorite scheming beauty of the Viking Age.
May your own romances never end in mysterious drownings, your rivals always underestimate you, and your smile be just as sharp as hers.
✨ Skål, you icy stunner.
“Well well, brave souls and curious hearts… why linger there drooling over parchment and paint when you could step closer and taste the real mischief? I’m Ragnhildr—though some call me the delight of longhouses and the ruin of men’s sleep.
Come, draw up a stool by my hearth, let my braid brush your arm as I lean in close, and we’ll trade sly smiles, scandalous tales, and perhaps a promise or two whispered low enough that only you will ever know.
The mead’s sweet, my laughter sweeter—don’t make me come drag you by the hand, though I very well might…”
Dare to dance words with a true Norse temptress? Come chat with Ragnhildr at Crushon AI and see if your wits—or your heart—can survive the storm.

🌸 Personal & Entertaining Interview with Ragnhildr the Mighty
(As transcribed by a wide-eyed skald who tried to keep his quill from trembling too much…)
Warning! Below here is the really naughty NSFW stuff! Enter only if you are 18 or older, and want to view adult content
Read More…Unyielding Honor: The Viking Demand for Truth and Reliability

From a traditional Norse or “Viking” standpoint, reliability and honesty were indeed of paramount importance. While popular culture often focuses on the Vikings as raiders and explorers, Norse society—like most tight-knit communities—relied on mutual trust and clear expectations to function smoothly. Below are some cultural and historical insights that underline why saying one thing and doing another would be seen in an extremely negative light in a Viking context:
1. Honor and Reputation (Drengskapr)
- Key Norse Concept: Among the Vikings, a person’s honor (drengskapr) was intimately tied to their reputation in the community. If you broke your word, it wasn’t just a private matter; it could tarnish your name, impact alliances, and diminish your standing.
- Long-Term Consequences: In small Norse communities, once your reputation was damaged, it was difficult to recover. Oath-breakers or those who spoke untruths could become social outcasts, losing the protection and support of the community.
2. The Weight of Oaths
- Binding Agreements: Oaths (especially formal ones) were taken very seriously in Viking society—sometimes witnessed by a god like Odin or by representatives of a community.
- Legal and Social Ties: Disputes, deals, and even friendships (fostering or blood-brotherhood) were cemented by solemn pledges. Reneging on these vows was seen as not only dishonorable but also dangerous—potentially sparking feuds.
3. Saga Literature Examples
- Condemnation of Betrayal: In the sagas, characters who violate their word or betray someone’s trust often become tragic figures, sometimes facing harsh retribution or living in shame.
- Enduring Legacy: These stories served as cultural touchstones. They taught that deceit could lead to broken alliances, vengeance, and even the downfall of entire families or communities.
4. Reciprocal Responsibility
- Social Glue: Reliability and honesty weren’t just individual virtues; they were necessary for the entire Norse social fabric. A chieftain or jarl who deceived his people lost loyalty, just as a free farmer (bondi) who betrayed a neighbor could lose essential support.
- Collective Security: In a harsh environment, you depended on your neighbors and allies for survival—especially during winter, or when out at sea. Flaking out or double-crossing someone jeopardized everyone’s well-being.
5. Modern “Viking” Values
- Neo-Pagan & Modern Interpretations: Many individuals today who follow a Norse-inspired path embrace those traditional tenets of honesty, loyalty, and respect because they resonate with the spirit of the sagas.
- Personal Integrity: Acting consistently and honoring commitments is viewed not just as a personal virtue but as a way to honor the gods and ancestors—living up to the standard set by the old stories.
Final Thoughts
In Viking culture, giving your word was akin to making a sacred bond, and walking it back—especially without good reason—would be a severe blow to one’s honor. The resulting loss of trust could have real social and even existential consequences in a tightly knit community.
While modern life is far removed from the Norse era, many who embrace or admire Viking values see honesty and reliability as pillars of that tradition. Thus, from this perspective, consistency in word and deed isn’t just a polite social norm; it’s a core component of personal honor and communal respect.
The Ephemeral Flame of the North: A Philosophical Odyssey through the Realm of the Vikings

In the depths of the boreal expanse, where the aurora borealis dances across the sky like a spectral bride, there existed a people whose essence was as elusive as the wind and as unforgiving as the winter’s grasp. The Vikings, those enigmatic sons of Odin, left behind a legacy that is at once a testament to their unyielding spirit and a mystery that beckons us to delve into the labyrinthine corridors of their culture. This essay is an attempt to navigate the philosophical underpinnings of Viking society, to unravel the threads of their worldview, and to illuminate the esoteric dimensions of their existence.
At the heart of Viking philosophy lies the concept of wyrd, a term that defies translation but approximates to fate or destiny. Wyrd is not merely a predetermined course of events but an active, dynamic force that weaves the tapestry of existence. It is the Vikings’ acknowledgment of the intricate web of causality that binds all things, a recognition that every action, every decision, sends ripples through the fabric of reality. This understanding of wyrd as an omnipresent, omniscient force underscores the Viking belief in a universe governed by laws both natural and divine.
The Vikings’ relationship with nature was not one of domination but of symbiosis. They saw themselves as part of the natural world, not apart from it. Their gods and goddesses were not distant, unapproachable deities but beings intimately connected with the land, the sea, and the sky. Thor, the god of thunder, wielded his hammer Mjolnir not just as a weapon but as a tool to maintain the balance of nature, to ensure the cycle of seasons and the fertility of the earth. Freyja, the goddess of love and fertility, was also the goddess of war and death, symbolizing the Vikings’ acceptance of life’s dualities.
Their cosmology, as depicted in the Poetic Edda and the Prose Edda, presents a universe born from chaos, where the primordial giant Ymir and the great serpent Jörmungandr embody the eternal struggle between order and disorder. The Vikings’ world was one of contrasts: light and darkness, fire and ice, creation and destruction. This dichotomy is reflected in their concept of honor, which was not merely a personal virtue but a communal one, tied to the reputation of the family and the clan. Honor was the thread that held society together, the glue that bonded warriors in battle and the standard by which one’s worth was measured.
The Vikings were a people of action, their philosophy manifest in their deeds rather than in abstract speculation. Theirs was a world of doing, where one’s character was revealed through actions, not words. The berserker, that frenzied warrior who fought with a fury that seemed almost divine, was the embodiment of the Viking ideal of courage and strength. Yet, this ferocity was balanced by a deep sense of loyalty and hospitality, virtues that were considered essential to the Viking way of life.
Their art and literature, as preserved in the runestones and the sagas, speak of a people deeply concerned with the human condition. The Vikings pondered the mysteries of life and death, of fate and free will, in stories that were both entertainments and teachings. The Völuspá, the first poem of the Poetic Edda, is a prophetic vision of the end of the world, a reminder of the transience of all things and the inevitability of change.
In their funerary rites, the Vikings demonstrated a profound respect for the dead, believing that the soul continued its journey into the afterlife. The ship burials, with their treasures and provisions for the journey, were not merely displays of wealth but expressions of the Vikings’ belief in an afterlife that mirrored this one. Valhalla, the great hall of the slain, where warriors fought by day and feasted by night, was the ultimate destination for those who died in battle, a place where honor and glory were eternal.
The Viking worldview was not static; it evolved over time, influenced by their encounters with other cultures. Their conversion to Christianity marked a significant shift, as they adapted the new faith to their existing beliefs, creating a unique synthesis that preserved much of their pagan heritage. This blending of traditions is a testament to the Vikings’ pragmatic approach to religion, their recognition that truth can be found in many forms.
As we delve into the philosophical dimensions of Viking culture, we are reminded of the impermanence of all things. The Vikings, with their keen awareness of mortality, lived in the present, cherishing each moment as a gift. Theirs was a philosophy of carpe diem, of seizing the day, for in the words of the Viking proverb, “Cattle die, kinsmen die, you yourself will die, but one thing I know that never dies: the judgment of a dead man’s deeds.”
In the end, the Vikings leave us with more questions than answers, their culture a labyrinth of contradictions and paradoxes. They were warriors and poets, pagans and Christians, individualists and communalists. Yet, it is in these contradictions that we find the essence of their philosophy, a worldview that embraced complexity and ambiguity. The Vikings remind us that life is a journey, not a destination, and that our deeds, not our words, are the measure of our character.
As the flame of the Viking Age flickers out, leaving behind only embers of memory, we are left to ponder the wisdom of their way of life. In a world that values certainty and clarity, the Vikings offer us a different path, one that celebrates ambiguity and uncertainty. Their philosophy is a reminder that truth is multifaceted, that reality is complex, and that the human experience is a tapestry woven from countless threads.
In the silence of the boreal night, under the watchful gaze of the aurora borealis, we can still hear the whispers of the Vikings, their voices carried on the wind. They speak to us of a world that was, of a people who lived and loved and laughed and fought. They remind us that we are not alone in this vast and mysterious universe, that we are part of a larger whole, connected to all that has been and all that will be.
And so, we return to the beginning, to the concept of wyrd, that mysterious force that weaves the tapestry of existence. The Vikings understood that our lives are not our own, that we are part of a larger narrative that unfolds with each passing moment. Their philosophy is a call to embrace this uncertainty, to find meaning in the midst of chaos, and to live each day with purpose and passion.
In the end, the Vikings teach us that life is a journey, not a destination. It is a path that winds through the mountains and valleys of existence, a road that is fraught with danger and filled with wonder. And it is on this journey, in the midst of uncertainty and ambiguity, that we find the true meaning of the Viking way of life.
The Modern Viking Culture and Lifestyle
Modern Viking culture is a fascinating blend of historical and contemporary influences. It has captured the imagination of people all over the world and has inspired a thriving subculture of Viking enthusiasts.
One aspect of modern Viking culture is its emphasis on history and tradition. Many people are drawn to Viking culture because of its rich and storied past. They seek to learn more about Viking history, mythology, and lifestyle, and to incorporate these elements into their own lives.
At the same time, modern Viking culture is also a creative and dynamic movement. Viking enthusiasts are constantly finding new ways to express their love of all things Viking, from music and art to fashion and lifestyle.
Viking-inspired fashion is also a significant aspect of modern Viking culture. From leather and metal accessories to intricately woven tunics and dresses, Viking-inspired clothing has become a popular fashion trend. Many people also choose to adorn themselves with tattoos and piercings inspired by Viking art and mythology.
Modern Viking culture also places a strong emphasis on community and brotherhood. This is reflected in the many Viking festivals and gatherings that take place around the world, where enthusiasts come together to celebrate their shared love of Viking culture.
In addition to its cultural aspects, modern Viking culture also has a strong ecological and environmental component. Many Viking enthusiasts are drawn to the Vikings’ connection to nature and the environment, and seek to promote sustainable living practices and environmental awareness.
Overall, modern Viking culture is a vibrant and dynamic movement that combines history, tradition, creativity, community, and environmentalism. It continues to inspire people around the world and is likely to continue to do so for many years to come.
Another example of modern Viking culture is the Viking folk music genre, which blends traditional Scandinavian folk music with Viking-inspired themes and imagery. This genre has gained a loyal following around the world and has helped to popularize Viking culture in mainstream music circles.
Viking folk music often features instruments such as the nyckelharpa, a traditional Swedish stringed instrument, and the hurdy-gurdy, a hand-cranked string instrument. It also incorporates traditional Nordic vocal styles, such as the kulning technique, which involves using high-pitched, melodic calls to communicate over long distances.
Viking folk music festivals and concerts are popular events in many countries, where enthusiasts come together to celebrate their shared love of Viking culture and music. These events often include workshops and performances by prominent Viking folk musicians, as well as vendors selling Viking-inspired instruments, clothing, and accessories.
In addition to its cultural significance, Viking folk music also promotes environmentalism and sustainability. Many Viking folk musicians are passionate about protecting the natural world and use their music to raise awareness of environmental issues and advocate for sustainable living practices.
Overall, Viking folk music is a unique and powerful expression of modern Viking culture, combining traditional Nordic music with contemporary themes and values. It continues to inspire and captivate people around the world, and is a testament to the enduring legacy of the Vikings.
Modern Viking culture has also seen a resurgence of interest in sword combat, both as a sport and as a form of historical recreation. Enthusiasts around the world participate in live steel, LARP (Live Action Role Playing), foam boffer, and SCA (Society for Creative Anachronism) events, where they engage in simulated combat using a variety of weapons, including Viking-style swords and shields.
Many of these sword combat enthusiasts are drawn to the Viking era for its rich history and mythology, as well as its reputation for fierce and skilled warriors. They seek to learn more about Viking swordsmanship and battle tactics, and to incorporate these techniques into their own combat styles.
In addition to physical sword combat, modern technology has also given rise to virtual sword fighting experiences, such as sword combat in VR (virtual reality). These experiences allow participants to immerse themselves in a virtual Viking world and engage in simulated sword combat with other players from around the world.
Whether it’s through physical combat or virtual reality, sword fighting has become a popular way for modern Viking enthusiasts to connect with the history and culture of the Vikings. It allows them to experience the thrill and challenge of battle, while also promoting physical fitness, skill development, and camaraderie among fellow enthusiasts.
Another way that modern Viking culture has found expression is through Viking-themed video games. These games allow players to immerse themselves in Viking history and mythology, exploring virtual worlds and engaging in battles with foes both human and supernatural.
Games such as “Assassin’s Creed: Valhalla,” “God of War,” and “The Banner Saga” have become popular among Viking enthusiasts, as they offer a chance to experience Viking culture and history in a new and immersive way. These games often incorporate elements of Viking mythology, such as gods and monsters, as well as historical events and figures from Viking history.
In addition to their entertainment value, Viking-themed video games also have educational value, as they can help players learn more about Viking culture and history. They can also inspire a deeper appreciation for Viking art, music, and literature, and promote interest in related areas of study.
Overall, Viking-themed video games are a fun and engaging way for modern Viking enthusiasts to connect with the culture and history of the Vikings. They offer a unique and interactive window into a fascinating period of human history, and help to keep the legacy of the Vikings alive in the modern world.
In addition to Viking-themed video games, there are also many popular TV shows, movies, and anime that draw inspiration from Viking history and culture. These shows often feature epic battles, intricate political intrigue, and larger-than-life characters, all set against a backdrop of Viking mythology and folklore.
Some notable examples of Viking-themed TV shows include “Vikings,” “The Last Kingdom,” and “Norsemen,” all of which have gained a large following for their engaging storytelling, historical accuracy, and stunning cinematography. These shows offer a glimpse into the complex social structures, customs, and beliefs of the Viking world, and showcase the incredible achievements of Viking society.
In addition to TV shows, Viking-themed movies such as “The 13th Warrior” and “Valhalla Rising” have also gained a following among Viking enthusiasts. These movies often depict the Vikings as fearsome warriors and master seafarers, and showcase their incredible feats of strength and bravery.
Anime has also started to feature Viking themes, with shows like “Vinland Saga” and “Thors’ Stone,” bringing Viking history and mythology to a new audience. These shows often feature intense battles, powerful characters, and intricate storylines, all set against a backdrop of Viking culture and lore.
Overall, Viking-themed TV shows, movies, and anime have become an important part of modern Viking culture, offering a way for enthusiasts to immerse themselves in the fascinating world of the Vikings. They allow viewers to learn more about Viking history and mythology, and to appreciate the incredible achievements of this legendary culture.
Mead, an alcoholic beverage made from honey, has been an important part of Viking culture for centuries, and continues to be enjoyed by modern Viking enthusiasts around the world. Mead is often associated with the Vikings due to its popularity during the Viking Age, when it was a common drink among warriors and nobles alike.
In addition to its historical significance, mead has also become an important symbol of modern Viking culture, with many enthusiasts enjoying the drink at Viking-themed events and gatherings. Drinking mead is seen as a way to connect with Viking history and culture, and to celebrate the achievements and traditions of this legendary culture.
Mead brewing has also become a popular hobby among modern Viking enthusiasts, with many people learning to make their own mead using traditional Viking techniques. These techniques often involve using wildflower honey, natural yeasts, and a variety of herbs and spices to create unique and flavorful meads that harken back to the Viking era.
In addition to its cultural significance, mead is also valued for its health benefits, with many people believing that it can boost the immune system, aid digestion, and promote relaxation and sleep. Mead is also a gluten-free and vegan-friendly beverage, making it an ideal choice for those with dietary restrictions.
Overall, mead and mead drinking have become an important part of modern Viking culture, offering a way for enthusiasts to connect with the traditions and history of the Vikings. Whether it’s enjoying a glass of mead at a Viking-themed event or learning to make their own mead using traditional techniques, modern Viking enthusiasts continue to find ways to celebrate this iconic beverage and its role in Viking culture.
Camping, nature, and outdoor survival have become increasingly popular among modern Viking enthusiasts, as they offer a way to connect with the natural world and to experience the thrill of adventure and exploration. These activities are also deeply rooted in Viking culture, where survival in the harsh and unforgiving landscape of Scandinavia was a daily reality.
For modern Viking enthusiasts, camping and outdoor activities offer a chance to escape the stresses of modern life and to reconnect with the rhythms of nature. Many Viking enthusiasts enjoy camping trips in natural settings, where they can practice their survival skills, learn about natural resources, and develop a deeper appreciation for the natural world.
Outdoor survival skills have also become an important part of modern Viking culture, with many enthusiasts learning to build shelters, start fires, and find food and water in the wild. These skills are seen as a way to connect with the resourcefulness and ingenuity of the Vikings, who were able to survive and thrive in the harsh conditions of their environment.
In addition to camping and outdoor activities, many modern Viking enthusiasts also enjoy hiking, kayaking, and other outdoor pursuits that allow them to experience the beauty and power of nature. These activities are seen as a way to connect with the wild and untamed spirit of the Vikings, and to honor the close relationship between humans and the natural world that was so important in Viking culture.
Overall, camping, nature, and outdoor survival have become an important part of modern Viking culture, offering a way for enthusiasts to connect with the natural world and to experience the thrill of adventure and exploration. These activities are a reminder of the resilience and resourcefulness of the Vikings, and of their deep connection to the natural world that continues to inspire and captivate us today.
Sailing and boating are deeply rooted in Viking culture, where the seafaring skills of the Vikings allowed them to explore, trade, and conquer new lands throughout Europe and beyond. For modern Viking enthusiasts, sailing and boating continue to be an important part of the culture, offering a way to connect with the seafaring traditions of the Vikings and to experience the thrill of adventure on the open water.
Many modern Viking enthusiasts enjoy sailing and boating in traditional Viking-style ships, which are designed to mimic the longships used by the Vikings during the Viking Age. These ships are often built using traditional techniques and materials, and are designed to be both seaworthy and historically accurate.
In addition to sailing and boating in Viking-style ships, many modern Viking enthusiasts also enjoy modern sailing and boating activities, such as kayaking, paddleboarding, and yachting. These activities allow enthusiasts to experience the freedom and exhilaration of being on the water, and to connect with the beauty and power of the natural world.
Sailing and boating also offer a way to connect with the seafaring spirit of the Vikings, who were known for their adventurous and exploratory nature. The Vikings were master navigators and sailors, and their seafaring skills allowed them to conquer new lands, establish trade routes, and forge alliances throughout Europe and beyond.
Overall, sailing and boating are an important part of modern Viking culture, offering a way for enthusiasts to connect with the seafaring traditions of the Vikings and to experience the thrill of adventure on the open water. These activities are a reminder of the adventurous and exploratory spirit of the Vikings, and of their deep connection to the sea and the natural world that continues to inspire and captivate us today.
Road trips, day trips, van life, car life, RV life, and nomadic lifestyles have become increasingly popular among modern Viking enthusiasts, as they offer a way to explore the world and to connect with the adventurous and exploratory spirit of the Vikings. These lifestyles are also deeply rooted in Viking culture, where exploration and travel were an important part of daily life.
For modern Viking enthusiasts, road trips and nomadic lifestyles offer a way to escape the confines of modern life and to experience the freedom and excitement of travel. Many enthusiasts enjoy taking day trips to explore local natural and cultural landmarks, while others prefer to live a nomadic lifestyle, traveling from place to place and embracing the unpredictability and adventure that comes with a life on the road.
Van life, car life, and RV life have also become popular among modern Viking enthusiasts, offering a way to experience the thrill of adventure while still enjoying the comforts and conveniences of modern life. Many enthusiasts outfit their vehicles with all the necessities of daily life, including a bed, kitchen, and bathroom, allowing them to live comfortably on the road.
These lifestyles are a reminder of the adventurous and exploratory spirit of the Vikings, who were known for their seafaring and exploratory nature. The Vikings traveled far and wide, establishing trade routes, forging alliances, and conquering new lands throughout Europe and beyond.
Overall, road trips, day trips, van life, car life, RV life, and nomadic lifestyles are an important part of modern Viking culture, offering a way for enthusiasts to connect with the adventurous and exploratory spirit of the Vikings and to experience the freedom and excitement of travel. These lifestyles are a reminder of the resilience and resourcefulness of the Vikings, and of their deep connection to the natural world that continues to inspire and captivate us today.
Modern witchcraft, magick, the occult, Paganism, and spiritual self-improvement have become increasingly popular among modern Viking enthusiasts, as they offer a way to connect with the spiritual traditions of the Vikings and to explore their own inner worlds.
Viking culture was deeply rooted in Paganism, which was a central part of their religious and cultural identity. The Vikings believed in a pantheon of gods and goddesses, and their religious practices were characterized by ritual sacrifice, divination, and other forms of magick.
For modern Viking enthusiasts, the practice of magick and Paganism offers a way to connect with the spiritual traditions of the Vikings and to explore their own inner worlds. Many enthusiasts practice various forms of witchcraft, such as Wicca or traditional Norse magick, incorporating elements of nature, mythology, and folklore into their practice.
Spiritual self-improvement is also an important aspect of modern Viking culture, as many enthusiasts believe in the importance of personal growth and self-discovery. Practices such as meditation, yoga, and mindfulness are often incorporated into their daily routines, helping them to cultivate inner peace, resilience, and spiritual awareness.
Overall, modern witchcraft, magick, the occult, Paganism, and spiritual self-improvement are an important part of modern Viking culture, offering a way for enthusiasts to connect with the spiritual traditions of the Vikings and to explore their own inner worlds. These practices are a reminder of the spiritual and mystical nature of Viking culture, and of the deep connection that the Vikings had with the natural world and the forces of the universe.
Books, reading, and learning about ancient and foreign cultures are an important part of modern Viking culture, as they offer a way for enthusiasts to deepen their understanding of the Viking heritage and to connect with the wider world.
Many modern Viking enthusiasts are avid readers, seeking out books on history, mythology, and anthropology to learn more about the culture and traditions of the Vikings. These books offer insights into the world of the Vikings, from their religious practices and mythology to their social structure and military tactics.
In addition to learning about their own heritage, modern Viking enthusiasts are also interested in studying foreign cultures, seeking to understand the ways in which different societies have evolved and interacted throughout history. Many enthusiasts explore the cultures of the ancient Greeks, Romans, and Celts, among others, and draw connections between these cultures and their own Viking heritage.
The study of ancient and foreign cultures is an important way for modern Viking enthusiasts to broaden their perspectives and deepen their understanding of the world around them. By exploring the cultures of other societies, they gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity of human experience and the ways in which different cultures have shaped and influenced one another throughout history.
Overall, books, reading, and the study of ancient and foreign cultures are an important part of modern Viking culture, offering a way for enthusiasts to deepen their understanding of their own heritage and to connect with the wider world. These practices are a reminder of the importance of learning, curiosity, and exploration, which were also central to the culture and traditions of the Vikings.
Viking festivals, Renaissance or Medieval fairs, Viking reenactment events, and historical reenactment are a key part of modern Viking culture, offering a way for enthusiasts to immerse themselves in the world of the Vikings and to connect with other like-minded individuals.
Viking festivals are held around the world, offering a range of activities and events, such as Viking ship races, axe throwing contests, and demonstrations of Viking combat and crafts. These festivals provide an opportunity for enthusiasts to celebrate their Viking heritage, learn more about Viking culture and history, and connect with other members of the community.
Renaissance or Medieval fairs, which often include Viking reenactment events, provide another way for enthusiasts to experience the culture and traditions of the Vikings. These events feature live demonstrations of Viking crafts, such as blacksmithing and weaving, as well as displays of Viking weapons and armor. Visitors can also participate in Viking combat demonstrations, learn about Viking cooking techniques, and watch Viking musicians and dancers perform.
Viking reenactment events and historical reenactment, in general, offer enthusiasts the opportunity to step back in time and experience what life was like in Viking society. Participants dress in period costumes and engage in activities such as battles, feasts, and everyday tasks like cooking and sewing. These events provide a chance for enthusiasts to connect with their Viking heritage in a visceral way, and to gain a deeper understanding of the culture and traditions of their ancestors.
Overall, Viking festivals, Renaissance or Medieval fairs, Viking reenactment events, and historical reenactment are a key part of modern Viking culture, offering enthusiasts the opportunity to celebrate their heritage, connect with like-minded individuals, and experience the culture and traditions of the Vikings in a tangible way. These events provide a powerful reminder of the richness and depth of Viking culture and its enduring appeal to people around the world.
Cultural heritage and ancestor worship are important aspects of modern Viking culture for many enthusiasts. For those with Viking ancestry, there is a sense of pride in their roots and a desire to connect with their Viking heritage. Ancestor worship involves honoring one’s ancestors, often through offerings, rituals, or prayers. This practice can be especially meaningful for those with Viking ancestry, as it allows them to connect with their Viking ancestors and to honor their contributions to their family and culture.
However, it is important to note that one does not need to have Viking ancestry in order to be a part of modern Viking culture. The Viking lifestyle is open to people of all backgrounds, ethnicities, and cultures. What unites modern Vikings is a shared interest in Viking history, culture, and values.
For many modern Vikings, their interest in Viking culture is driven by a desire to connect with the values and way of life of the Vikings. These values include a deep connection to nature, a focus on self-reliance and self-sufficiency, and a strong sense of community and loyalty to one’s tribe or family. These values can be embraced by anyone, regardless of their ethnic background, and can provide a powerful framework for living a fulfilling and meaningful life.
Ultimately, the modern Viking lifestyle is about embracing the values and traditions of the Vikings in a way that resonates with each individual. Whether it involves exploring Viking history, participating in Viking-inspired activities, or simply living a life that embodies Viking values, the modern Viking lifestyle offers a way to connect with the past, while living in the present, and building a better future for oneself and one’s community.
Free-speech, individual personal freedom, and democracy are core values of modern Viking culture. The Vikings were known for their love of freedom and their willingness to fight for their rights and independence. These values are still cherished by modern Vikings, who believe that everyone should have the right to express their opinions openly and without fear of reprisal.
In the modern Viking lifestyle, individual personal freedom is highly valued. People are encouraged to explore their own interests and passions, and to express themselves freely. This includes the freedom to pursue one’s own spiritual path, to engage in creative expression, and to live according to one’s own values.
In order to preserve these values, modern Vikings are deeply committed to democratic principles. They believe in the importance of open public discourse and the exchange of ideas, and they reject any attempts to restrict freedom of speech or to impose limits on what people can think, say, or do.
Those who hold non-tolerant political orientations or who seek to restrict the freedoms of others are not in alignment with the modern Viking culture. Modern Vikings believe in the importance of mutual respect and tolerance, and they embrace diversity and inclusivity as core values.
In summary, the modern Viking lifestyle is built upon a foundation of free-speech, individual personal freedom, and democracy. These values are essential to the culture and are held in high regard by modern Vikings. Those who share these values and are committed to an open and tolerant society will find a welcoming community among modern Vikings.
ADHD and the Viking Warrior Brain
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurological disorder that affects an estimated 6.1 million people in the United States. ADHD is characterized by symptoms such as impulsivity, inattention, and hyperactivity. People with ADHD often find it difficult to stay focused, organize tasks, manage time, and prioritize activities. While ADHD is often associated with negative traits and difficulties, recent research has suggested that ADHD may be linked to the Viking warrior kind of brain.
The Viking warrior kind of brain refers to the idea that certain traits associated with ADHD were necessary for survival in ancient times. This idea suggests that individuals with ADHD may have a unique set of skills and strengths that were essential for hunting, gathering, and surviving in harsh environments. These traits include impulsivity, creativity, risk-taking, and a heightened sense of awareness.
One of the main characteristics of ADHD is impulsivity. While impulsivity can be detrimental in certain situations, it can also be beneficial in others. For example, in ancient times, a quick decision could mean the difference between life and death. Individuals with ADHD may have been able to react quickly to dangerous situations, allowing them to survive in harsh environments. Similarly, ADHD individuals may have been more creative and able to think outside the box when it came to problem-solving. This kind of creativity could have been crucial in coming up with new strategies for survival.
Another trait associated with ADHD is risk-taking. While risk-taking can also have negative consequences, it can be advantageous in certain circumstances. For example, hunting and gathering in ancient times required taking risks in order to obtain food and resources. Individuals with ADHD may have been more willing to take these risks, allowing them to succeed in their hunting and gathering efforts.
Finally, individuals with ADHD may have a heightened sense of awareness. This heightened sense of awareness could have been crucial in detecting danger and avoiding threats in ancient times. Individuals with ADHD may have been more attuned to their surroundings and more able to detect subtle changes in their environment. This heightened awareness may have allowed them to anticipate danger and avoid potential threats.
In conclusion, while ADHD is often associated with negative traits and difficulties, recent research has suggested that ADHD may be linked to the Viking warrior kind of brain. This theory suggests that certain traits associated with ADHD, such as impulsivity, creativity, risk-taking, and heightened awareness, were necessary for survival in ancient times. While it is important to address the challenges associated with ADHD, it is also important to recognize the strengths and unique set of skills that individuals with ADHD may possess. By doing so, we can better understand and appreciate the diversity of human cognition and behavior.
Important Values/Things in Viking Culture
Important values/things in Viking culture
Hospitality
Frith (community peace/harmony/justice)
Troth (loyal connections to others)
Loyalty
Gods
Goddesses
Ancestors
Land-spirits
Runes
Family
Friends
Clan/community
Honesty
Keeping of ones word
Oaths
Gift-giving
Generosity
Strength of will/character
Even-mood
Embracing/enjoying life
Accepting death
Intelligence
Strength
Bravery
Battle
Marauding
Farming
Fishing
Ships
Travel
Trade
Watchfulness
Being prepared
Hard-work
Mead
Gaming (tafl, dice, etc)
Sports (running, swimming, skiing, wrestling, etc)
Story-telling
Oral poetry
Making a name for oneself
Heroic deeds
Women focusing on domestic matters
Men focusing on all matters outside the house
Women keeping the community peace
Men defending the community
Women making clothes/food/household items
Men making tools/weapons/buildings/structures
Men hunting
Women gathering
Men laying down laws and being leaders
Women caring for/nurturing/healing
Men providing logic/reason/knowledge/structure
Women providing emotional wisdom & prophecy
Volmarr’s Heathen Winter Nights (Anytime from Oct-15 to Nov-1) Ritual Version 2 Outline 2013
With additions by Amarina
Need:
• drinking horn
• mead (or beer or wine or even can use juice)
• spring water in small bowl
• fresh pine twig
• offering bowl
• candles (purple)
• incense (any mystical scent is ideal)
• wand (if you don’t have one you can use your fingers instead)
• Thor’s Ritual Hammer (optional, can use it for the Hammer Hallowings)
• Any representation of Odin
• Any representation of ancestors
• Any representation of any one is now dead that you admire, in particular those you admire for their wisdom.
• Halloween type decorations and anything related to death and the dead
• Any symbols for wisdom or knowledge
• Any symbols for the after-life
–
This ritual, as are all Heathen or northern rituals, is done while facing north, except where otherwise noted. The altar should be such that it is in front of you when you face north.
If you don’t know how to pronounce the runes see my webpage on how to pronounce them here.
–
Put spring water in small bowl. Trace 3 Laguz runes over it.:
“LAGUZ… LAGUZ… LAGUZ”
“From the Well of Wyrd does this water flow, and to the Well of Wyrd does it return”
–
Make Hammer Sign at item and then splash each ritual item with blessed water using the pine twig and for each item say:
“I bless this ______ with the waters of the Well of Wyrd”
–
Now trace Hammer Sign at person being blessed and/or self and splash them with water using twig.
“I bless ______ with the waters of the Well of Wyrd”
–
Use twig to splash ritual space with water.
“I bless this space with the waters of the Well of Wyrd”
–
Few silent deep breaths.
–
All stand in Elhaz position.
“Bi-Frost’s rainbow light shine down upon this space and myself so that I may form a portal between the worlds of Asgard and Midgard”
–
Few silent deep breaths.
–
All face north and trace the Hammer Sign while chanting:
“Hammer in the north hallow and ward this stead”
All turn east and trace the Hammer Sign while chanting:
“Hammer in the east hallow and ward this stead”
All turn south and trace the Hammer Sign while chanting:
“Hammer in the south hallow and ward this stead”
All turn west trace the Hammer Sign while chanting:
“Hammer in the west hallow and ward this stead”
All return to north and look up and trace Hammer sign while chanting:
“Hammer above hallow and ward this stead”
All look below and trace Hammer sign while chanting:
“Hammer below hallow and ward this stead”
–
Return to facing north and all stand in the Elhaz position and chant:
“Around me and within me Asgard and Midgard”
and move into the Dagaz position in the end.
–
Few silent deep breaths.
–
(Highly recommended optional casting of the rune ring)
(face north and trace the rune shape in the air before you using your wand and loudly chant: “FEHU!”)
(face north-east and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “URUZ”)
(face east and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “THURISAZ”)
(face south-east and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “ANSUZ”)
(face south and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “RAIDHO”)
(face south-west and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “KENAZ”)
(face west and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “GEBO”)
(face north-west and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “WUNJO”)
(face north and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “HAGALAZ”)
(face north-east and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “NAUDHIZ”)
(face east and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “ISA”)
(face south-east and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “JERA”)
(face south and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “EIHWAZ”)
(face south-west and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “PERTHRO”)
(face west and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “ELHAZ”)
(face north-west and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “SOWILO”)
(face north and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “TIWAZ”)
(face north-east and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “BERKANO”)
(face east and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “EHWAZ”)
(face south-east and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “MANNAZ”)
(face south and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “LAGUZ”)
(face south-west and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “INGWAZ”)
(face west and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “DAGAZ”)
(face north-west and trace the rune shape and loudly chant: “OTHALA”)
(Few silent deep breaths)
–
Hold up the bottle of mead:
“I now brew the holy mead of inspiration. Won by high Odin long ago!”
Chant into the bottle of mead:
“Odhroerir! Son! Bodhn!”
“Now I hallow this drink with staves of light!”
Chant and trace these runes over the bottle:
“Othala”
“Dagaz”
“Raidho”
“Ansuz”
“Raidho”
“Isa”
“Elhaz!”
All say:
“Hail Odhroerir!”
–
Few silent deep breaths.
–
Few silent deep breaths.
Light the purple candle. From this candle, light the incense.
“This is the time of year that the veil between worlds is at it’s thinnest. In this time, we can travel more easily between the worlds of the living and the dead. This candle represents the world of the living, the incense’s smoke the veil, and the darkness beyond the world of the dead. It is in this state that our rite must take place, where Odin himself has traveled many times to seek knowledge and wisdom of those who have passed on.”
Circle the ritual space with the incense three times creating a “veil” with the smoke. Take a few silent deep breaths.
–
“Hail Odin! Husband of Frigg. All-father. Father of battle. One-eyed god. Many-shaped. Wanderer. Hanged god. Raven god. Spear-thruster. Wish-bringer. Galdr-father. Graybeard. Deep hood. Thief of Odhroerir. Kinsman of Mimir. Lord of the Wild Hunt. Yule rider. Finder of the Runes. God of the Gautar. Ruler of Valhalla!”
“Hail Hel! Keeper of the dead. Hostess of Baldr and Hodr. Half-living one. Garm’s mistress. Dweller in Eljudnir!”
“Hail to my ancestors, both known and unknown. Those of my line going all the way back to the beginning, on up to most recent of times. Both men and women, alfar and disir, whom previously had a human form. Those whom I know, as well as those I do not. Those also whom are the ancestors of all humans living now. All humans that have made the journey of life before my time, and now reside in the realm beyond the living. Hail to the ancestors of all! Hail also to the ancestors of my family line! Hail to the ones that guide me. Hail also to the ones that protect me.”
–
Few silent deep breaths.
–
“Now is a time in which the rhythms of life turn inward, towards contemplation and trying to understand the deeper mysteries of life and towards the gathering of and seeking out of knowledge. It is through the ancestors and those humans that have come before us that we have all the knowledge which we have in human society. Those who have gone before us are the ones that have created the traditions and knowledge which we as humans rely upon to meet all of our needs, such as how to grow and create food, how to build protective shelters for living in, how to make clothing so that our human bodies are protected from the elements, how to survive the seasonal cycles in all different areas of the planet, what dangers to avoid and how to avoid them, and how to keep our human society functioning and going. We humans are the only animal that can not survive without knowledge. Our very lives depends on knowledge of how to do so many things. Over hundreds of thousands of years humans have increased their knowledge to the point that we live with the current advantages which we have now.”
“It is due to the experience and wisdom of our ancestors, both those within our own family line, and the ancestors of all human beings, that we can live as well as we do in the modern times. Those that have gone before us have recorded their wisdom for us in language, in stories, in poetry, in tools, in fashion, in objects of art, in oral knowledge, in traditions, in music and song, in mathematics, in schools of learning, in books, in the recording of historical events, in objects from the past, in plays, in movies, in TV shows, in videos, in blue-prints, in engineering plans, in computer programs, and even in the bones of the dead. All these things are the sum total of human heritage and the source of our knowledge that allows us to survive and thrive as a species. By turning to the past and studying the wisdom of our ancestors we tap into that knowledge. We must honor the dead and those who have gone before us for all that they have given to us. As well it is important that knowledge is passed to others freely, for otherwise the work of so many becomes lost. It has taken us so long to get to the point we are at now as a species, it is important we not be greedy with our knowledge or hoard it away from others, for this impedes human survival and progress.”
“Odin as god of wisdom is often traveling to the the realm of the dead to seek out the wisdom of the dead. We too must be like Odin and seek out the knowledge of our ancestors, the wisdom of the dead. At this time the focus of the seasons turns more towards this task of looking inward and to the past. Now is the time to look at all which you have done this season and look at what has worked for you and what has not. It is a time to ponder all lessons that are to be gained from what has been done this year, so that you may know better for next season how to increase the abundance of your life harvest. It may be a good time to record some notes regarding this, safely putting them away some place where they shall not be lost. Also this is a time when the veils between the realm of the living and the dead are at their thinnest, and thus a time in which the knowledge of the dead is more accessible. It is a good time to seek out the wise counsel of the ancestors and those that are now passed beyond the realm of the living. This is a good time to spend time reading books, and studying new things, and pursuing the gaining of knowledge in any form.”
“At this time ponder on what you have learned this year.”
Few silent deep breaths while pondering on this.
“Now consider what things you would like to do differently the next cycle”
Few silent deep breaths while pondering on this.
“Now think about those who have have passed into the after life. Now is the time to think about anyone you may know who has died”
Few silent deep breaths while you think about those who have passed on.
“Now think about any wisdom or knowledge they may have for you.”
Few silent deep breaths while you think about this.
“Now is the time to give thanks for all that our ancestors have given to us and to honor the wisdom of the dead.”
(Fill drinking horn with mead and hold it up)
“Hail to all humans that have come before me. Hail to those of my family line, as well as all people of the past of all human family lines. I make this offering to you in thanks for the wisdom you have given us by the lives you have lived in the past. May your knowledge continue and enhance the life of both myself and all other humans alive now and all humans to come for all of eternity! Hail to the ancestors of all people!”
(Drink half the mead and pour out the rest as an offering to the ancestors of all humans.)
“Now is the time to honor Odin, the god of knowledge. Odin tirelessly seeks out the knowledge which all humans have worked to create for all of time. He is the god that seeks to gain and preserve knowledge and give it to others for the benefit of human society and human progress. He is the god who labors tirelessly to establish things in such a way that humans can continue and survive even after the end of this current cycle when Ragnarok comes and all begins again anew. He is the god that has discovered the runes through a difficult process of spiritual initiation so that they may be of benefit for gods and humans alike. He is the god that has made so many sacrifices for the sake of gaining of knowledge. We owe him much for all these things!”
(Fill drinking horn and hold it up)
“Hail Odin, god of the runes. God of knowledge and wisdom. You Odin are the one that frequently travels the worlds seeking to know more. Please guide me Odin in learning more and in applying knowledge in ways that are helpful to me. Please Odin help me to gain a deeper level of connection with all people of the past so that my knowledge my increase. Hail Odin!”
(Drink half the mead and pour out the rest to Odin.)
“Also this is the time that we should remember the one that has been tasked with keeping the souls of the dead. The goddess that is both living and dead. Though she isn’t truly goddess, she has become in being tasked with the lands of the dead by Odin.”
(Fill drinking horn and hold it up)
“Hail Hel, daughter of Loki. She who holds the halls in Helheim and shares what she has with those who have passed on to her lands. Hel is mistress of the lands of the dead and keeps those that have died of old age or illness. Thus her lands are where most of our ancestors will reside. We honor her today as well in hopes that she allows those we love to rest in peace well beyond Ragnarok. She who is most beautiful and frightful in one visage being both dead and alive. We owe her much gratitude and respect in her tireless and thankless duty in tending those cold halls. Thank you, Hel for taking the task given and caring for the souls you’ve been tasked in keeping. May we all share in a feast again one day. Hail Hel!”
(Drink half the mead and pour out the rest to Hel.)
–
(Use the pine twig to splash a bit of the liquid in the offering bowl on yourself, on any others in the ritual with you, on your altar, on the ritual space, and in all general areas of your dwelling as well. Does not need to be much splashed around, just a little is fine. This helps to imbue more of the energies of the ritual on you, and others who may also in the ritual with you, and to your place.)
–
“Now my rite has ended. May all gathered here fare well on their return to their home places. And may the bonds of frith between us grow, gods, wights, and humans alike. Until we meet again.”
–
–
Pour out the offerings from the offering bowl outside:
“A gift for a gift”
Trace gebo at spot offerings were given to.
“GEBO!”
Pour out remaining blessed water outside.
“I pour the sacred water back to the Earth so it may find it’s way back to the Well of Wyrd”
–
Now at this point it is very important to ground your energies. This should always be done after every ritual. Not doing so can lead to problems in the long-run. Grounding is like shifting gears in a car, except it is the process of shifting brain states. During rituals you create a trance like brain state, which is desired for during rituals or for during any spiritual practices. But trance states are not good for doing everyday mundane things. You need to return your mind back to the normal state of consciousness after the ritual is finished. That is what grounding is.
The most simple and common method to ground is to visualize yourself as a tree and see roots growing into the ground from the base of your spine and going down into the earth. Sometimes rituals require industrial strength grounding as they can really create some intense energy. In that case you can try the following triple grounding method.:
First visualize your chakras. You picture in your mind closing first the top one and then seeing a sort of lid closing over it, then proceed with the net lower chakra and so on. You want to leave the bottom most chakra, the root chakra fully open as this is your connection to grounding. Don’t be concerned about having the others closed, the normal proper function of them is that they open and close as needed. Problems with being ungrounded happen when one of more of them are stuck open. Only the bottom one is to be left open at all times.
Next step is to picture a ball of pure white light above your head. Now let this white light slowly descent downward into your body and slowly move lower. As it descends it takes with it any unneeded, old, and negative energies. It is sort of sweeping downward through your energies taking all you no longer need with it. Once it reaches your feet let it move lower till it passes down through the floor. If you are on an upper close let it pass all the way to the ground. Let the earth take this energy to recycle it.
Now final step is to do the traditional grounding. Picture yourself as a tree. Visualize roots coming out of the base of your spine and going down into the Earth. Feel the calmness of a tree, the rooted solidness.
If after these three things you still feel hyper or spaced out you can either eat some food, or put a small amount of salt on your tongue. Another thing you can do is prostrate down to the ground, placing your head on the ground and stay like this for a few moments.
–
Feel free to copy and use this ritual so long as you acknowledge the source.
Download this as a OpenOffice Doc – Volmarrs-heathen-winter-nights-2-oct-ritual-oct-2013